友情支持
如果您觉得这个笔记对您有所帮助,看在D瓜哥码这么多字的辛苦上,请友情支持一下,D瓜哥感激不尽,😜
|
|
有些打赏的朋友希望可以加个好友,欢迎关注D 瓜哥的微信公众号,这样就可以通过公众号的回复直接给我发信息。

公众号的微信号是: jikerizhi。因为众所周知的原因,有时图片加载不出来。 如果图片加载不出来可以直接通过搜索微信号来查找我的公众号。 |
322. 零钱兑换
给你一个整数数组 coins,表示不同面额的硬币;以及一个整数 amount,表示总金额。
计算并返回可以凑成总金额所需的 最少的硬币个数。如果没有任何一种硬币组合能组成总金额,返回 -1。
你可以认为每种硬币的数量是无限的。
示例 1:
输入:coins = [1, 2, 5], amount = 11 输出:3 解释:11 = 5 + 5 + 1
示例 2:
输入:coins = [2], amount = 3 输出:-1
示例 3:
输入:coins = [1], amount = 0 输出:0
提示:
-
1 <= coins.length <= 12 -
1 <= coins[i] <= 231 - 1 -
0 <= amount <= 104
思路分析
解题思路
-
这种找路径,找方法的题一般可以使用回溯法来解决,回溯法也可以说是树形图法,解题的时候使用类似于树状图的结构,使用 自顶而下 的方法。
-
而在回溯法中,如果含有很多的重复的计算的时候,就可以使用记忆化的搜索,将可能出现的重复计算大状态使用一个数组来保存其值,在进行重复的计算的时候,就可以直接的调用数组中的值,较少了不必要的递归。
-
使用了记忆化搜索后,一般还可以进行优化,在记忆化搜索的基础上,变成 自底而上 的动态规划。
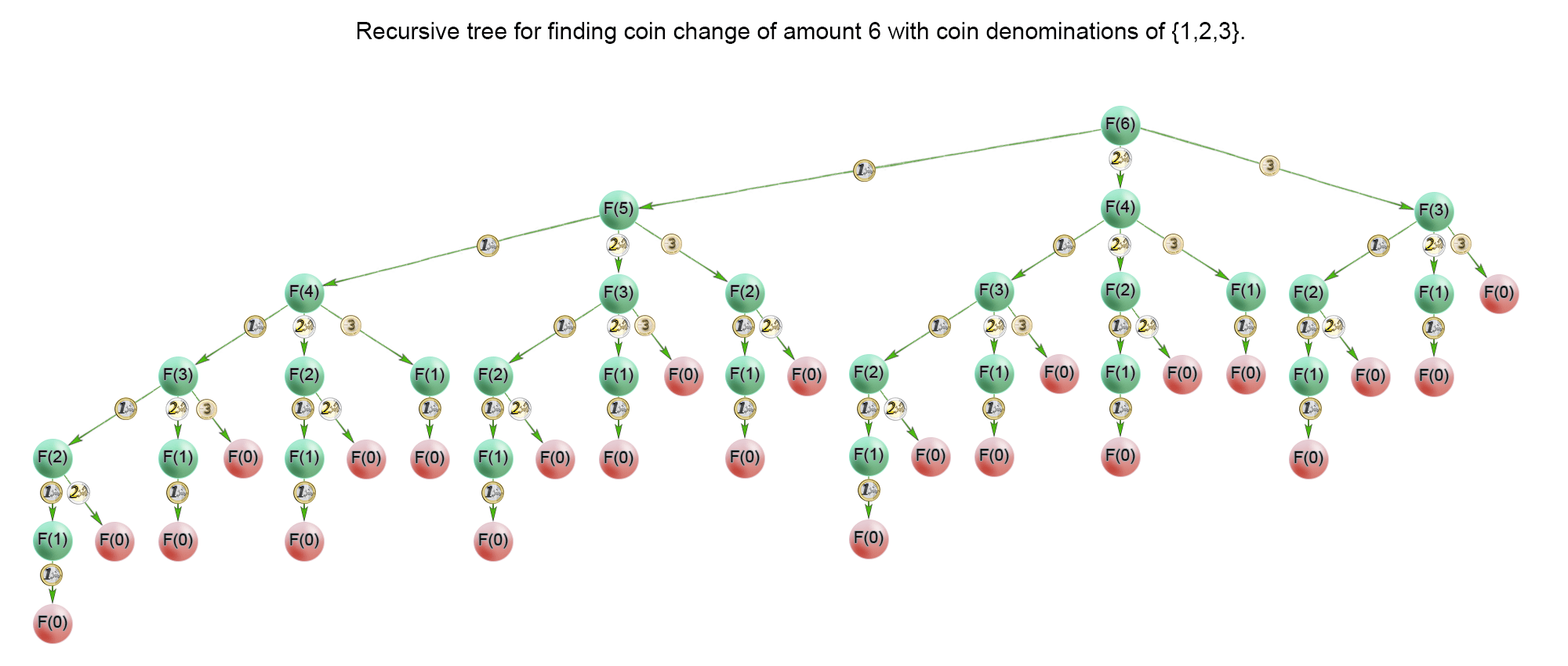
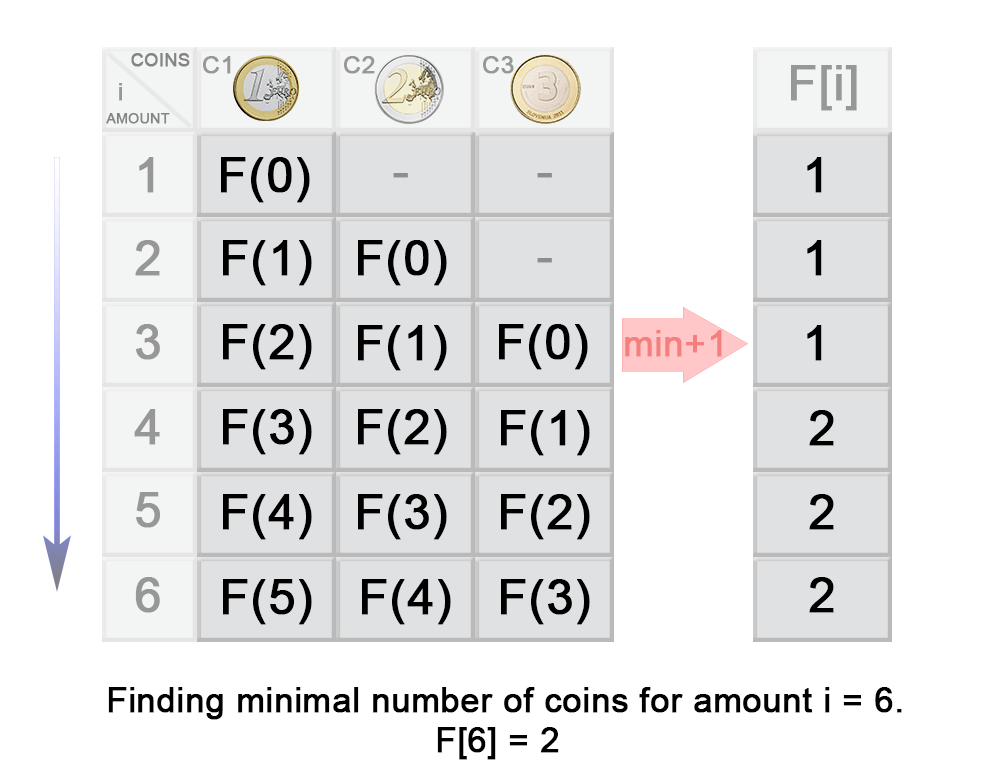
F(3) =min(F(3−c1),F(3−c 2),F(3−c3))+1
=min(F(3−1),F(3−2),F(3−3))+1
=min(F(2),F(1),F(0))+1
=min(1,1,0)+1
=1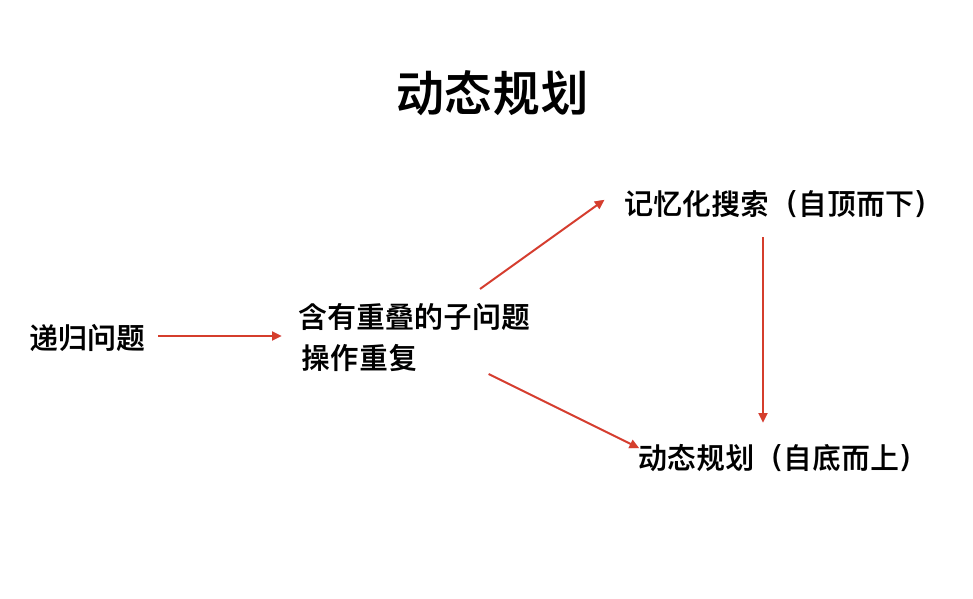
与 416. 分割等和子集 对比,体会一下 0/1 Knapsack 0/1 背包 与 Unbounded Knapsack 完全背包 的差异:
| 特征 | 0/1 背包 (0/1 Knapsack) | 完全背包 (Unbounded Knapsack) |
|---|---|---|
核心定义 |
每种物品仅有一件 |
每种物品有无限件 |
二维状态转移方程 |
\$dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i-1][j-w]+v)\$ |
\$dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-w]+v)\$ |
状态依赖 |
依赖上一轮 ( |
依赖本轮 ( |
一维优化遍历顺序 |
逆序遍历背包容量 |
正序遍历背包容量 |
Java核心代码差异 |
|
|
-
一刷
-
二刷(暴力穷举)
-
二刷(动态规划(莫名其妙解法))
-
二刷(动态规划)
-
三刷(动态规划)
-
四刷
-
五刷
-
六刷
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
/**
* Runtime: 91 ms, faster than 6.13% of Java online submissions for Coin Change.
*
* Memory Usage: 42.7 MB, less than 5.33% of Java online submissions for Coin Change.
*
* Copy from: https://leetcode.com/problems/coin-change/solution/[Coin Change solution - LeetCode]
*
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2020-01-26 22:16
*/
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
return coinChange(coins, amount, new int[amount]);
}
private int coinChange(int[] coins, int current, int[] count) {
if (current < 0) {
return -1;
}
if (current == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (count[current - 1] != 0) {
return count[current - 1];
}
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int coin : coins) {
int res = coinChange(coins, current - coin, count);
if (0 <= res && res < min) {
min = res + 1;
}
}
count[current - 1] = (min == Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? -1 : min;
return count[current - 1];
}
/**
* Runtime: 427 ms, faster than 5.00% of Java online submissions for Coin Change.
*
* Memory Usage: 115.5 MB, less than 5.33% of Java online submissions for Coin Change.
*/
public int coinChangeDpWithMemo(int[] coins, int amount) {
int count = dpWithMemo(coins, new HashMap<>(), amount, amount);
if (count > amount) {
return -1;
}
return count;
}
public int dpWithMemo(int[] coins, Map<Integer, Integer> memo, int amount, int current) {
if (current == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (current < 0) {
return amount;
}
List<Integer> counts = new ArrayList<>();
for (int coin : coins) {
int newCoin = current - coin;
int count;
if (memo.containsKey(newCoin)) {
count = memo.get(newCoin);
} else {
count = dpWithMemo(coins, memo, amount, newCoin) + 1;
memo.put(newCoin, count);
}
counts.add(count);
}
return Collections.min(counts);
}
/**
* Time Limit Exceeded
*/
public int coinChangeDp(int[] coins, int amount) {
int count = dp(coins, amount, amount);
if (count > amount) {
return -1;
}
return count;
}
private int dp(int[] coins, int amount, int current) {
if (current == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (current < 0) {
return amount;
}
List<Integer> counts = new ArrayList<>();
for (int coin : coins) {
counts.add(dp(coins, amount, current - coin) + 1);
}
return Collections.min(counts);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
/**
* 最笨的方法:暴力穷举,超时
*
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2024-06-27 21:12
*/
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
if (amount < 0) {
return -1;
}
if (amount == 0) {
return 0;
}
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int coin : coins) {
int cnt = coinChange(coins, amount - coin);
if (cnt == -1) {
continue;
}
result = Math.min(result, cnt + 1);
}
return result == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : result;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
/**
* 参考 左程云《程序员代码面试指南》。完全没看明白。
*
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2024-06-27 21:12
*/
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amt) {
if (coins == null || coins.length == 0 || amt < 0) {
return -1;
}
int N = coins.length;
int[][] dp = new int[N + 1][amt + 1];
// 设置最后一排的值,除了 dp[N][0] 外,其他都是-1
for (int i = 1; i <= amt; i++) {
dp[N][i] = -1;
}
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 从底向上计算每一行
printMatrix(dp);
for (int rest = 0; rest <= amt; rest++) { // 每一行都从左向右
dp[i][rest] = -1; // 初始时,先设置 dp[i][rest] 的值无效。这样省去了一次遍历设置每一行的操作
if (dp[i + 1][rest] != -1) { // 下面的值如果有效
dp[i][rest] = dp[i + 1][rest]; // 先设置成下面的值
}
// 如果坐标的位置不越界且有效
if (rest - coins[i] >= 0 && dp[i][rest - coins[i]] != -1) {
if (dp[i][rest] == -1) { // 如果之前下面的值无效
dp[i][rest] = dp[i][rest - coins[i]] + 1;
} else { // 说明下面和左边的值都有效,取最小的
dp[i][rest] = Math.min(dp[i][rest], dp[i][rest - coins[i]] + 1);
}
}
}
}
System.out.println("最后结果");
printMatrix(dp);
return dp[0][amt];
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
/**
* 参考 https://leetcode.cn/problems/coin-change/solutions/132979/322-ling-qian-dui-huan-by-leetcode-solution/[322. 零钱兑换 - 官方题解^]
*
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2024-06-27 21:12
*/
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amt) {
if (coins == null || coins.length == 0 || amt < 0) {
return -1;
}
int max = amt + 1;
int[] dp = new int[max];
Arrays.fill(dp, max);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= amt; i++) {
for (int coin : coins) {
if (coin <= i) {
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coin] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[amt] > amt ? -1 : dp[amt];
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2025-04-09 11:36:55
*/
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int max = amount + 1;
// 1、确定 dp 数组(dp table)以及下标的含义
// 兑换 i 元钱,最少需要多少个货币
int[] dp = new int[max];
// 3、dp 数组如何初始化
// 由于求最小值,则初始化比金额大一的数
// 注:初始化为 Integer.MAX_VALUE 时,需要处理溢出问题
Arrays.fill(dp, max);
dp[0] = 0;
// 4、确定遍历顺序,先金额从小到大开始遍历,再逐个货币进行尝试
// 注:这样遍历,就可以尽可能多次使用大大额货币,比如
// f(11) = f(11-5) + 1 = (f(11-5-5) + 1) + 1 = 3
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
for (int coin : coins) {
// 2、确定递推公式:f(n+1) = min{f(n+1), f(n) + 1}
if (coin <= i) {
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coin] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[amount] >= max ? -1 : dp[amount];
// 原始解法,当做一个对比放在这里吧
// if (amount == 0) {
// return -1;
// }
// Arrays.sort(coins);
// int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
// Arrays.fill(dp, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// dp[0] = 0;
// for (int coin : coins) {
// for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
// for (int j = 1; j * coin <= i; j++) {
// int pre = dp[i - j * coin];
// if (pre < Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
// dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], pre + j);
// }
// }
// }
// }
// return dp[amount] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2025-10-06 20:30:27
*/
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
Arrays.sort(coins);
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp, amount + 1);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
for (int coin : coins) {
if (coin > i) {
break;
}
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coin] + 1);
}
}
return dp[amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2025-10-09 19:57:15
*/
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int MAX = amount + 1;
// dp[j] 表示凑成金额 j 所需的最少硬币数
int[] dp = new int[MAX];
// 初始化 dp 数组为一个最大值,方便后面取 min
Arrays.fill(dp, MAX);
dp[0] = 0; // 凑成金额0需要0个硬币
for (int coin : coins) {
// 完全背包:正序遍历容量
for (int j = coin; j <= amount; j++) {
// 决策:不使用这枚coin vs 使用这枚coin
dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - coin] + 1);
}
}
return dp[amount] == MAX ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2025-12-17 20:27:45
*/
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp, amount + 1);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int coin : coins) {
for (int i = coin; i <= amount; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coin] + 1);
}
}
return dp[amount] == amount + 1 ? -1 : dp[amount];
}