友情支持
如果您觉得这个笔记对您有所帮助,看在D瓜哥码这么多字的辛苦上,请友情支持一下,D瓜哥感激不尽,😜
|
|
有些打赏的朋友希望可以加个好友,欢迎关注D 瓜哥的微信公众号,这样就可以通过公众号的回复直接给我发信息。

公众号的微信号是: jikerizhi。因为众所周知的原因,有时图片加载不出来。 如果图片加载不出来可以直接通过搜索微信号来查找我的公众号。 |
40. 组合总和 II
给定一个候选人编号的集合 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用 一次 。
注意:解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8, 输出: [ [1,1,6], [1,2,5], [1,7], [2,6] ]
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5, 输出: [ [1,2,2], [5] ]
提示:
-
1 <= candidates.length <= 100 -
1 <= candidates[i] <= 50 -
1 <= target <= 30
思路分析
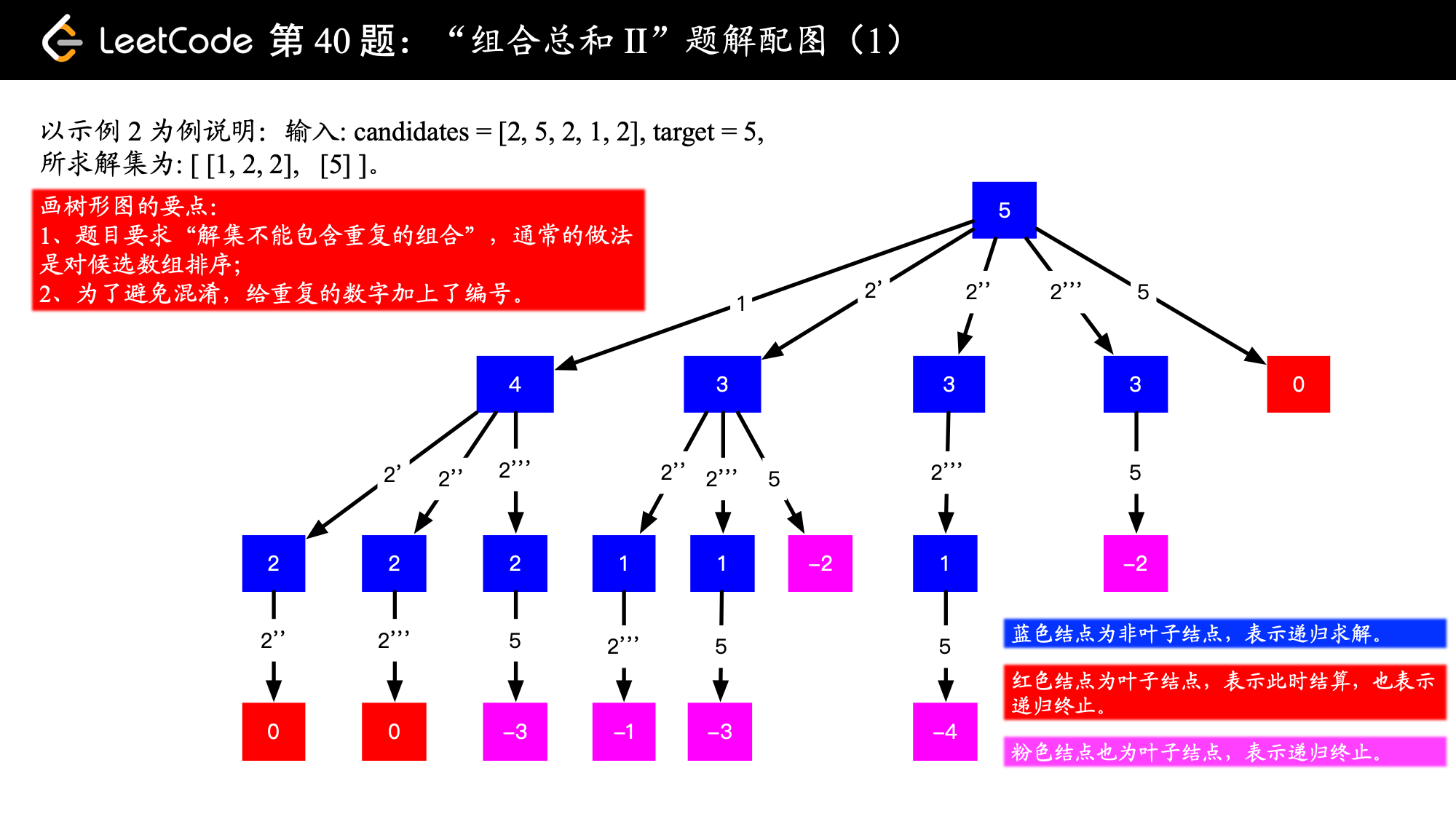
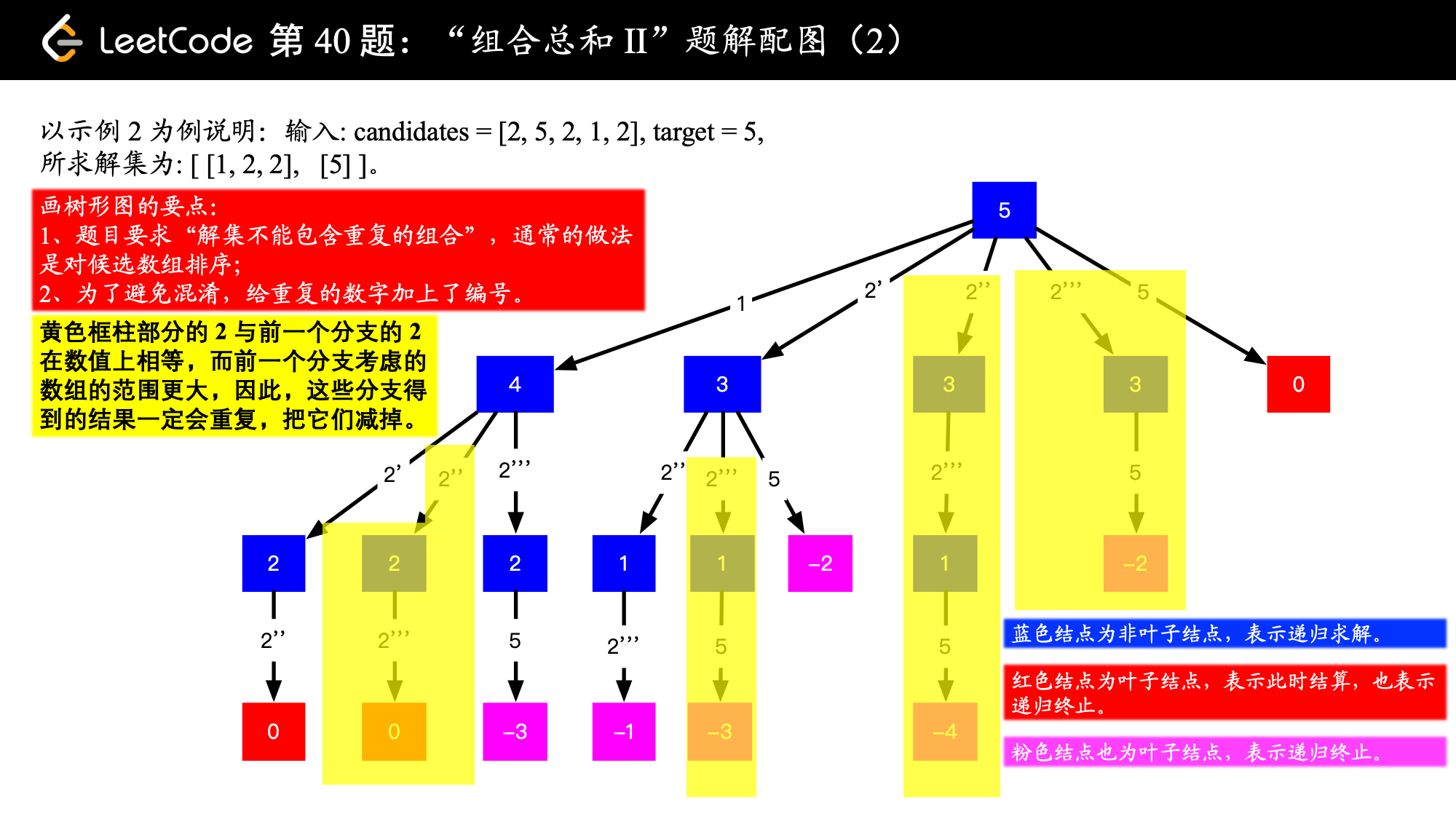
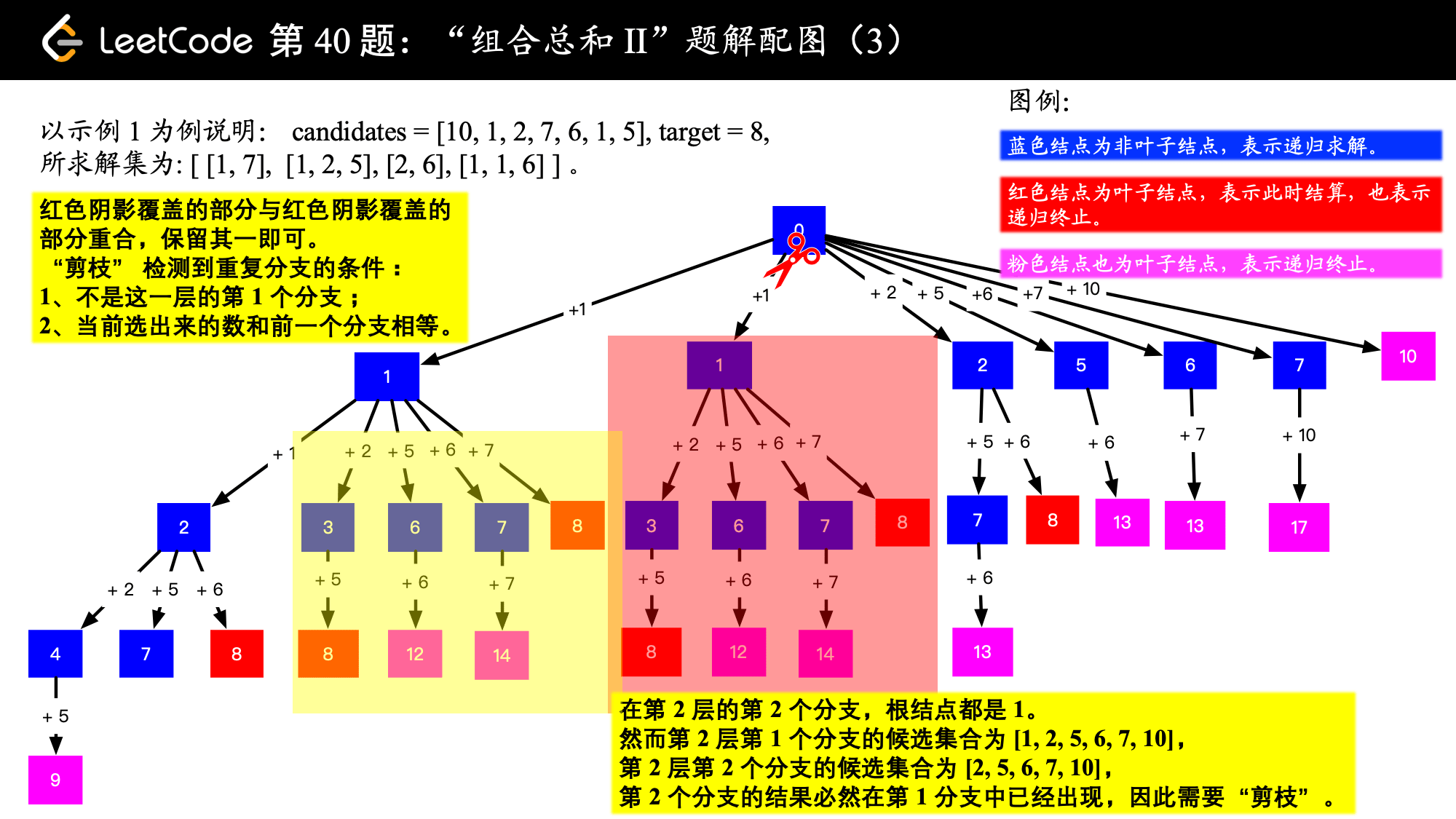
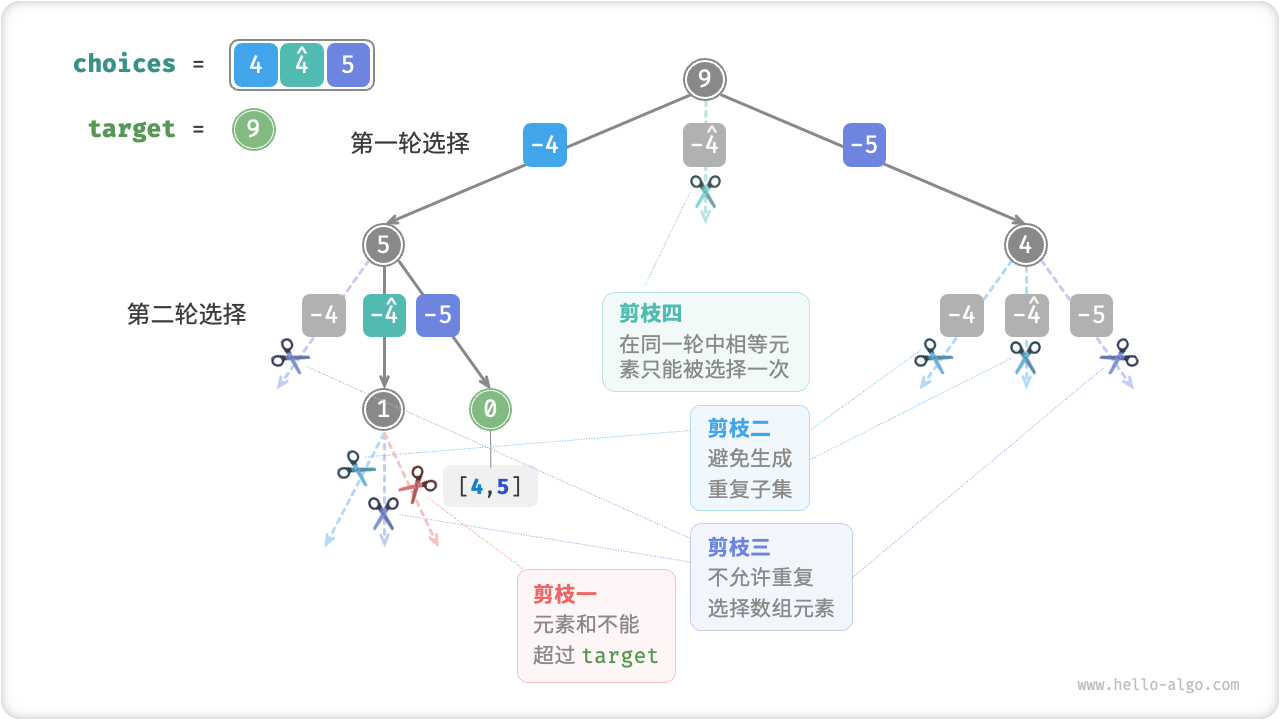
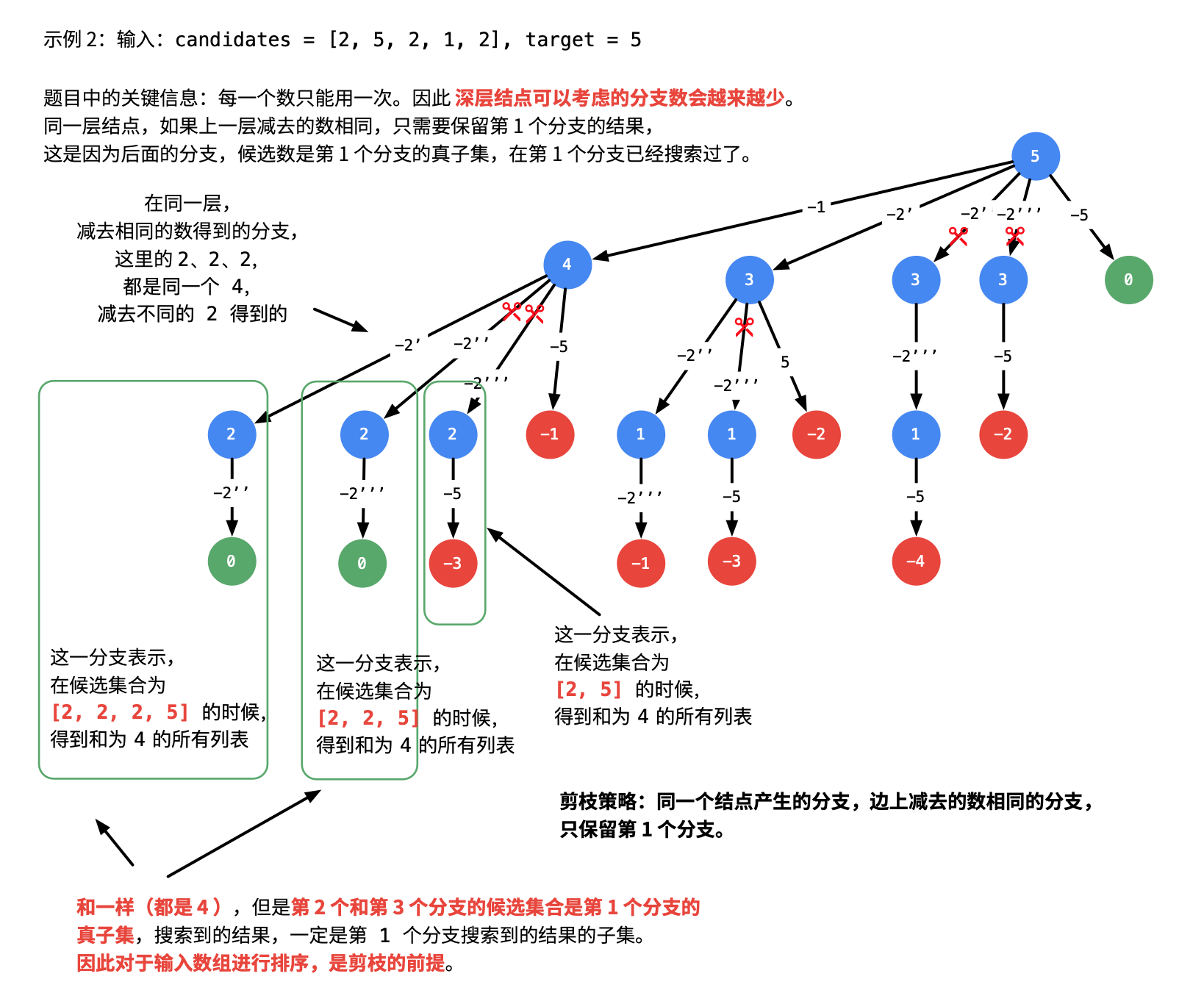

这道题的关键是由于候选值不能重复使用,所以需要向下传递起始位置。可以对比一下 39. 组合总和 的处理上的不同之处。
思考一下解决重复值时是怎么剪枝的?
-
一刷
-
二刷
-
三刷
-
四刷
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
/**
* Runtime: 2 ms, faster than 100.00% of Java online submissions for Combination Sum II.
* Memory Usage: 39.5 MB, less than 54.74% of Java online submissions for Combination Sum II.
*
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2020-01-27 19:20
*/
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
if (Objects.isNull(candidates) || candidates.length == 0) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
Arrays.sort(candidates);
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
backtrack(candidates, 0, target, result, new ArrayDeque<>());
return new ArrayList<>(result);
}
private void backtrack(int[] candidates, int beginIndex, int target,
List<List<Integer>> result, Deque<Integer> current) {
if (target == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(current));
return;
}
for (int i = beginIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {
int candidate = candidates[i];
if (target < candidate) {
break;
}
if (!current.isEmpty() && current.peekLast() > candidate) {
continue;
}
if (beginIndex < i && candidate == candidates[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
current.addLast(candidate);
// 因为元素不可以重复使用,这里递归传递下去的是 i + 1 而不是 i
backtrack(candidates, i + 1, target - candidate, result, current);
current.removeLast();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2024-07-10 16:52:25
*/
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backtrack(candidates, result, 0, target, new ArrayList<>());
return result;
}
private void backtrack(int[] candidates, List<List<Integer>> result,
int start, int target, List<Integer> path) {
// 子集和等于 target 时,记录解
if (target == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
// 剪枝二:从 start 开始遍历,避免生成重复子集
// 剪枝三:从 start 开始遍历,避免重复选择同一元素
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
// 剪枝一:若子集和超过 target ,则直接结束循环
// 这是因为数组已排序,后边元素更大,子集和一定超过 target
if (target < candidates[i]) {
break;
}
// 剪枝四:如果该元素与左边元素相等,说明该搜索分支重复,直接跳过
if (start < i && candidates[i - 1] == candidates[i]) {
continue;
}
path.add(candidates[i]);
// 进行下一轮选择
backtrack(candidates, result, i + 1, target - candidates[i], path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2025-04-25 17:47:05
*/
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
backtrack(candidates, target, result, 0, new ArrayList<>());
return result;
}
private void backtrack(int[] candidates, int target,
List<List<Integer>> result, int start, List<Integer> path) {
if (target == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
int num = candidates[i];
if (target < num) {
break;
}
if (start < i && candidates[i - 1] == candidates[i]) {
continue;
}
path.add(num);
backtrack(candidates, target - num, result, i + 1, path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2024-09-16 17:31:07
*/
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
backtrack(candidates, target, result, path, 0);
return result;
}
private void backtrack(int[] candidates, int target,
List<List<Integer>> result,
List<Integer> path, int index) {
if (target == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++) {
int num = candidates[i];
// 已经超量了,则直接返回
if (num > target) {
return;
}
// 同一层,相同的数字只能选一次。否则,就会产生重复的组合。
if (i > index && candidates[i - 1] == candidates[i]) {
continue;
}
path.add(num);
backtrack(candidates, target - num, result, path, i + 1);
path.removeLast();
}
}