友情支持
如果您觉得这个笔记对您有所帮助,看在D瓜哥码这么多字的辛苦上,请友情支持一下,D瓜哥感激不尽,😜
|
|
有些打赏的朋友希望可以加个好友,欢迎关注D 瓜哥的微信公众号,这样就可以通过公众号的回复直接给我发信息。

公众号的微信号是: jikerizhi。因为众所周知的原因,有时图片加载不出来。 如果图片加载不出来可以直接通过搜索微信号来查找我的公众号。 |
429. N-ary Tree Level Order Traversal
Given an n-ary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
Example 1:

Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
Output: [[1],[3,2,4],[5,6]]Example 2:
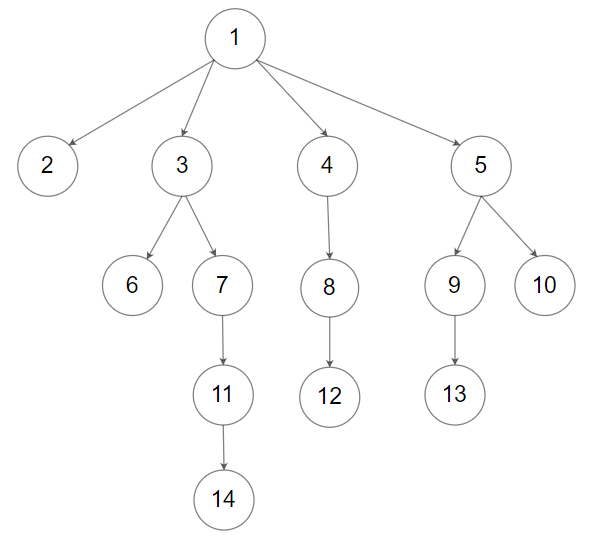
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
Output: [[1],[2,3,4,5],[6,7,8,9,10],[11,12,13],[14]]Constraints:
-
The height of the n-ary tree is less than or equal to
1000 -
The total number of nodes is between
[0, 10^4]
思路分析
直接广度优先遍历,每层独立处理即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2024-06-25 15:17:45
*/
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>(size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node node = queue.poll();
level.add(node.val);
if (node.children != null) {
node.children.forEach(queue::offer);
}
}
result.add(level);
}
return result;
}
static class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
}