友情支持
如果您觉得这个笔记对您有所帮助,看在D瓜哥码这么多字的辛苦上,请友情支持一下,D瓜哥感激不尽,😜
|
|
有些打赏的朋友希望可以加个好友,欢迎关注D 瓜哥的微信公众号,这样就可以通过公众号的回复直接给我发信息。

公众号的微信号是: jikerizhi。因为众所周知的原因,有时图片加载不出来。 如果图片加载不出来可以直接通过搜索微信号来查找我的公众号。 |
60. Permutation Sequence
The set [1,2,3,…,n] contains a total of n! unique permutations.
By listing and labeling all of the permutations in order, we get the following sequence for n = 3:
-
"123"
-
"132"
-
"213"
-
"231"
-
"312"
-
"321"
Given n and k, return the kth permutation sequence.
Note:
-
Given
nwill be between 1 and 9 inclusive. -
Given
kwill be between 1 and n! inclusive.
Input: n = 3, k = 3 Output: "213"
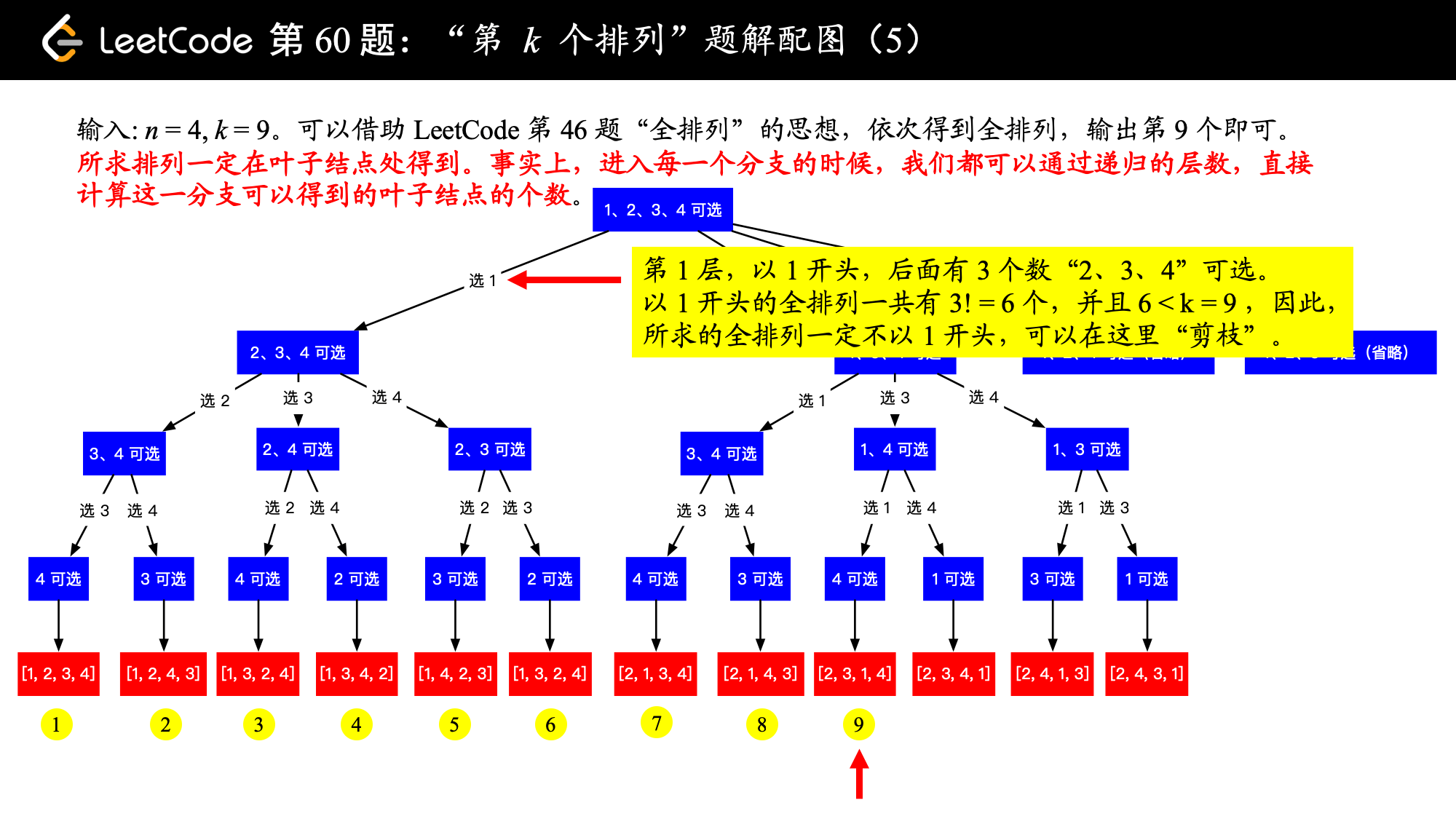
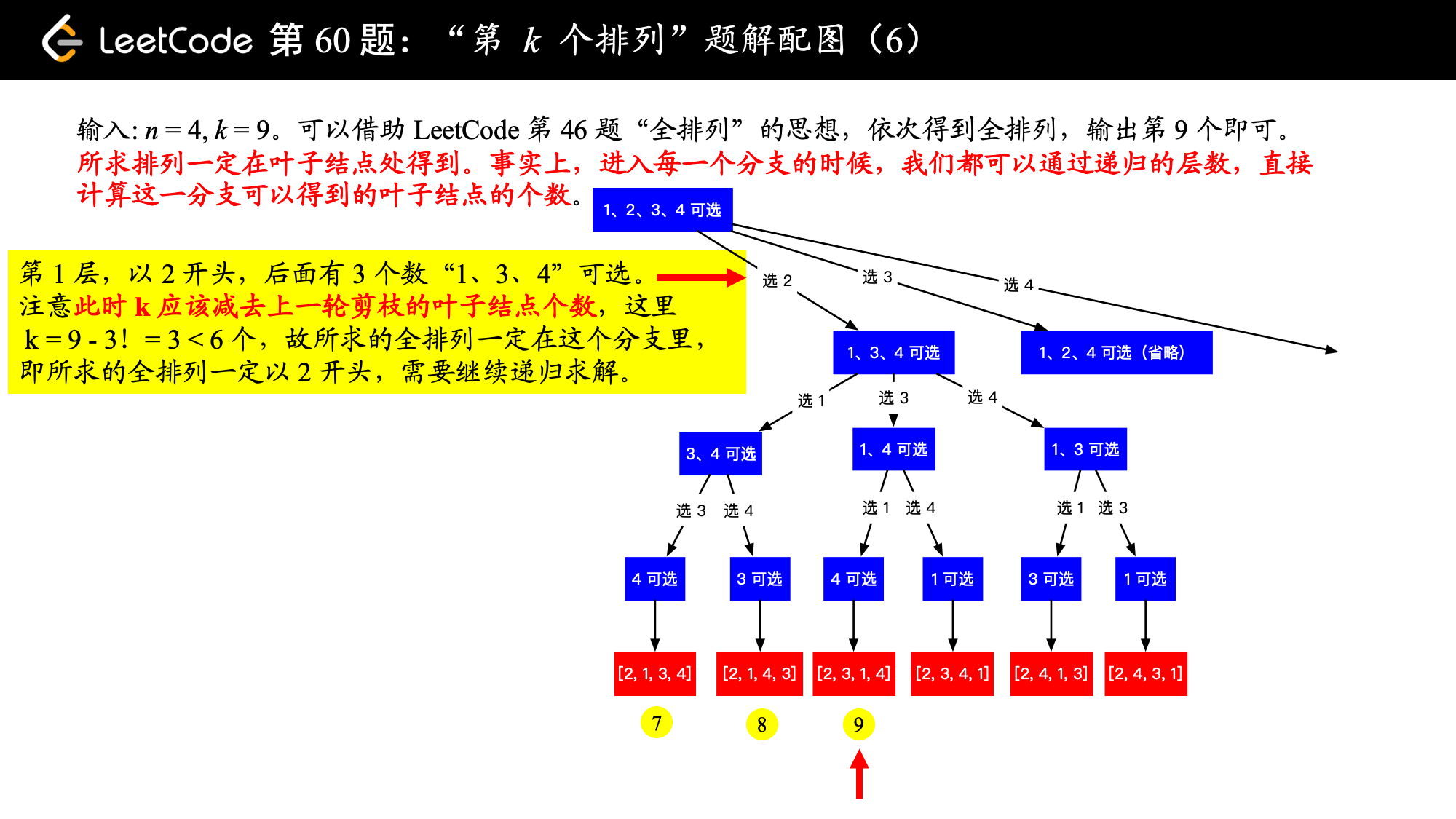
Input: n = 4, k = 9 Output: "2314"
参考资料
The set [1,2,3,…,n] contains a total of n! unique permutations.
By listing and labeling all of the permutations in order, we get the following sequence for n = 3:
-
"123" -
"132" -
"213" -
"231" -
"312" -
"321"
Given n and k, return the kth permutation sequence.
Note:
-
Given n will be between 1 and 9 inclusive.
-
Given k will be between 1 and n! inclusive.
Example 1:
Input: n = 3, k = 3 Output: "213"
Example 2:
Input: n = 4, k = 9 Output: "2314"
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
/**
* Runtime: 1 ms, faster than 99.26% of Java online submissions for Permutation Sequence.
* Memory Usage: 37.2 MB, less than 20.83% of Java online submissions for Permutation Sequence.
*
* Copy from: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutation-sequence/solution/hui-su-jian-zhi-python-dai-ma-java-dai-ma-by-liwei/[深度优先遍历 + 剪枝、双链表模拟 - 第k个排列 - 力扣(LeetCode)]
*/
private boolean[] used;
private int[] factorial;
private int n;
private int k;
private List<Integer> path;
public String getPermutation(int n, int k) {
this.n = n;
this.k = k;
used = new boolean[n + 1];
factorial = new int[n + 1];
factorial[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
factorial[i] = factorial[i - 1] * i;
}
path = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(0);
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
for (Integer integer : path) {
builder.append(integer);
}
return builder.toString();
}
private void dfs(int index) {
if (index == n) {
return;
}
int cnt = factorial[n - 1 - index];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (used[i]) {
continue;
}
if (cnt < k) {
k -= cnt;
continue;
}
path.add(i);
used[i] = true;
dfs(index + 1);
}
}
/**
* Time Limit Exceeded
*/
public String getPermutationRecursion(int n, int k) {
List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
nums.add(i);
}
List<String> permutations = new LinkedList<>();
permutations(nums, 0, permutations);
ArrayList<String> sp = new ArrayList<>(permutations);
sp.sort(Comparator.naturalOrder());
return sp.get(k - 1);
}
private void permutations(List<Integer> nums, int index, List<String> result) {
if (index == nums.size()) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(index);
for (int num : nums) {
builder.append(num);
}
result.add(builder.toString());
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < nums.size(); i++) {
Collections.swap(nums, i, index);
permutations(nums, index + 1, result);
Collections.swap(nums, i, index);
}
}