友情支持
如果您觉得这个笔记对您有所帮助,看在D瓜哥码这么多字的辛苦上,请友情支持一下,D瓜哥感激不尽,😜
|
|
有些打赏的朋友希望可以加个好友,欢迎关注D 瓜哥的微信公众号,这样就可以通过公众号的回复直接给我发信息。

公众号的微信号是: jikerizhi。因为众所周知的原因,有时图片加载不出来。 如果图片加载不出来可以直接通过搜索微信号来查找我的公众号。 |
113. 路径总和 II
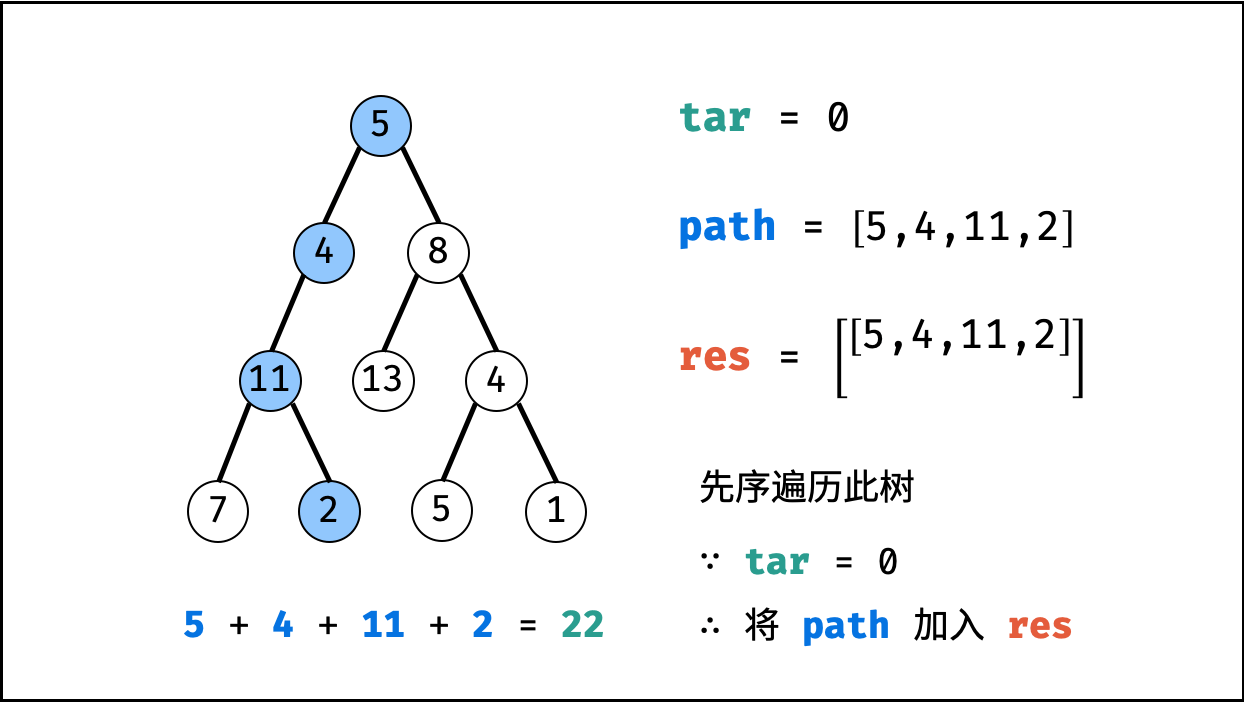
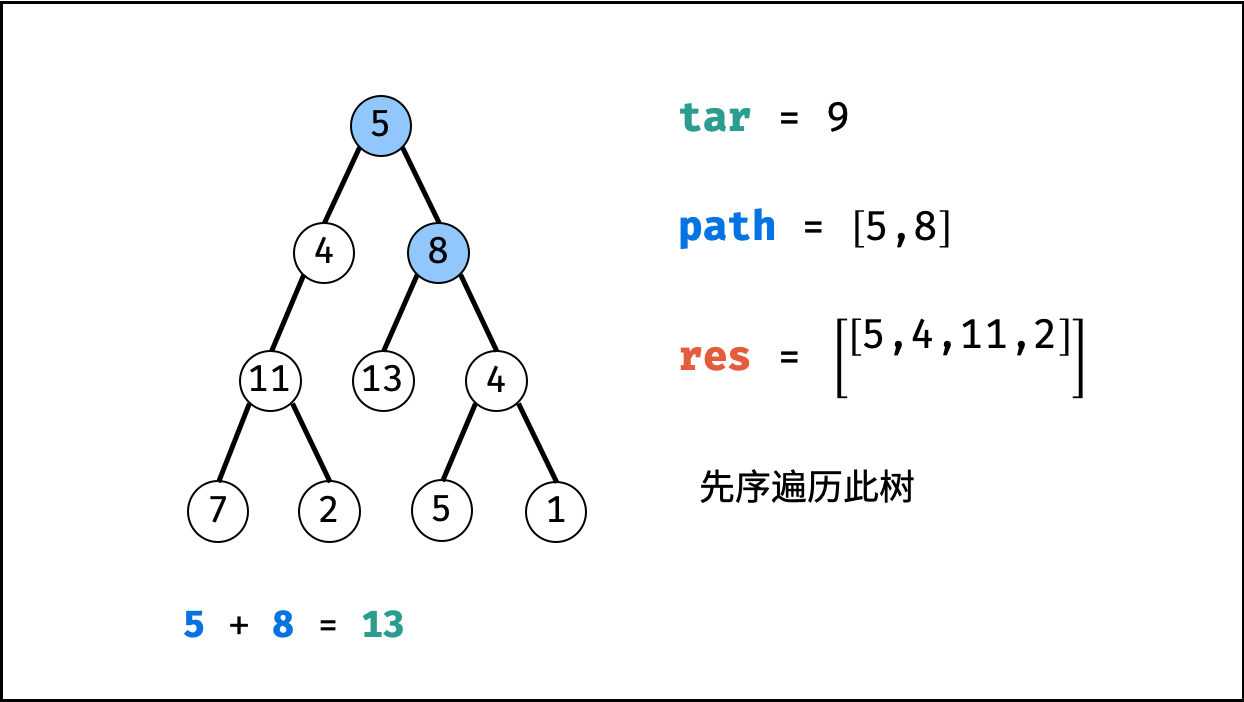
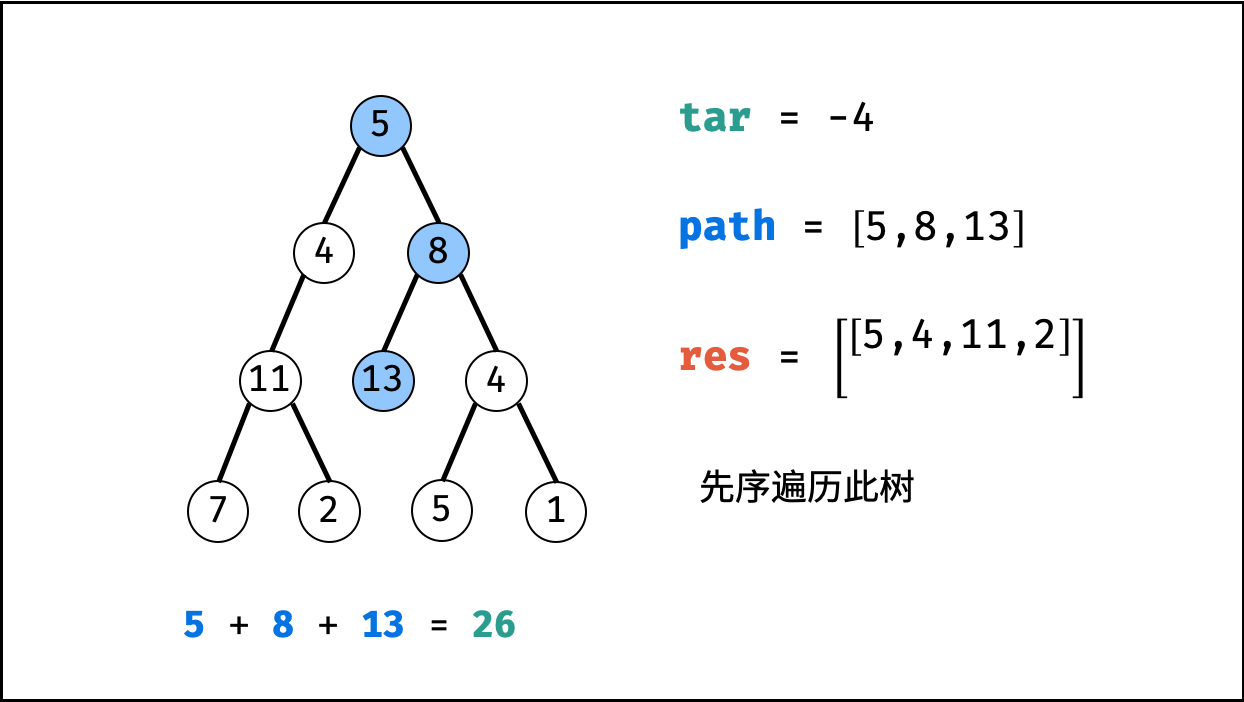
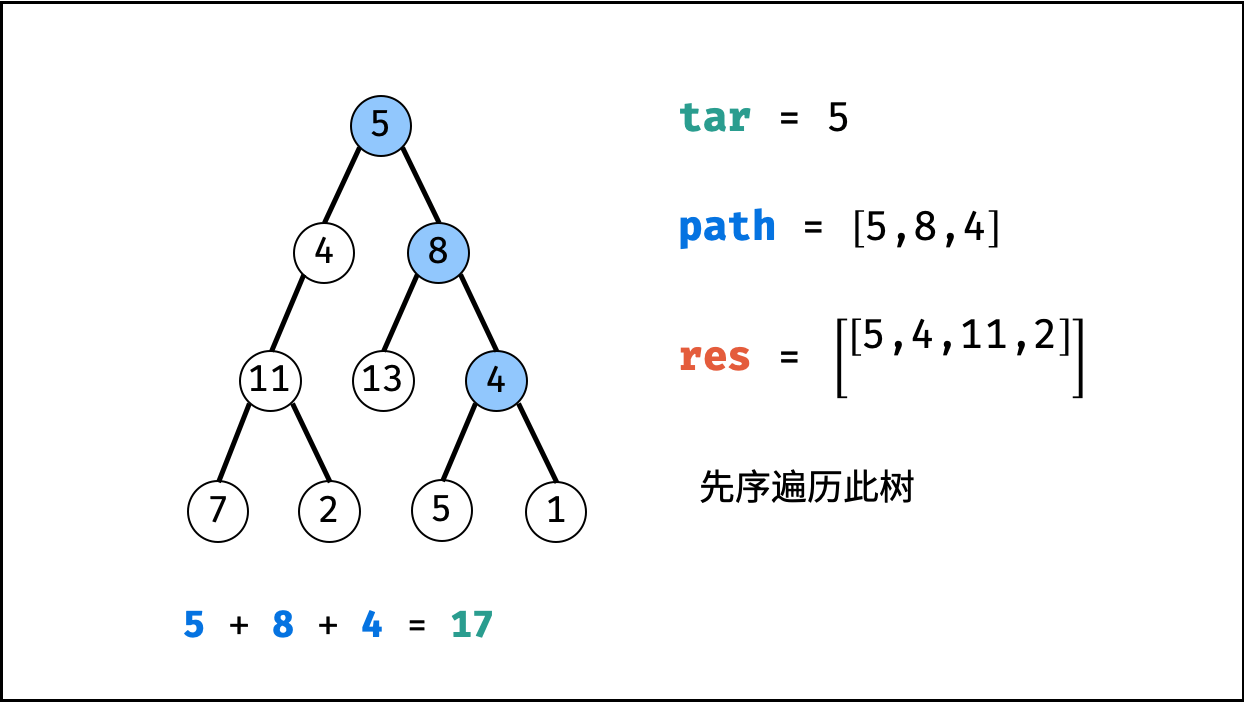
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
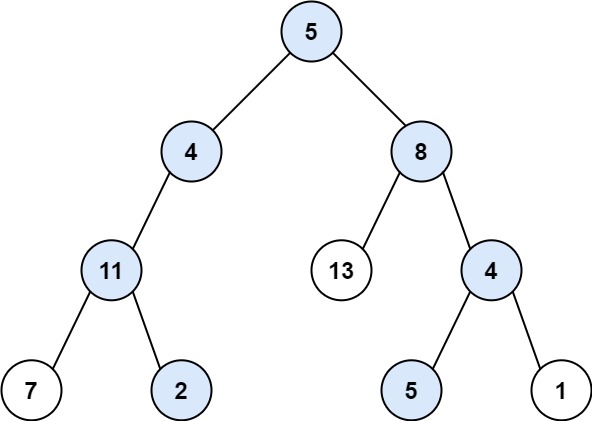
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22 输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
示例 2:
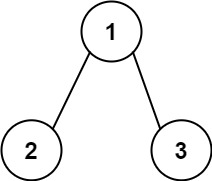
输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,2], targetSum = 0 输出:[]
提示:
-
树中节点总数在范围
[0, 5000]内 -
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000 -
-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
解题分析
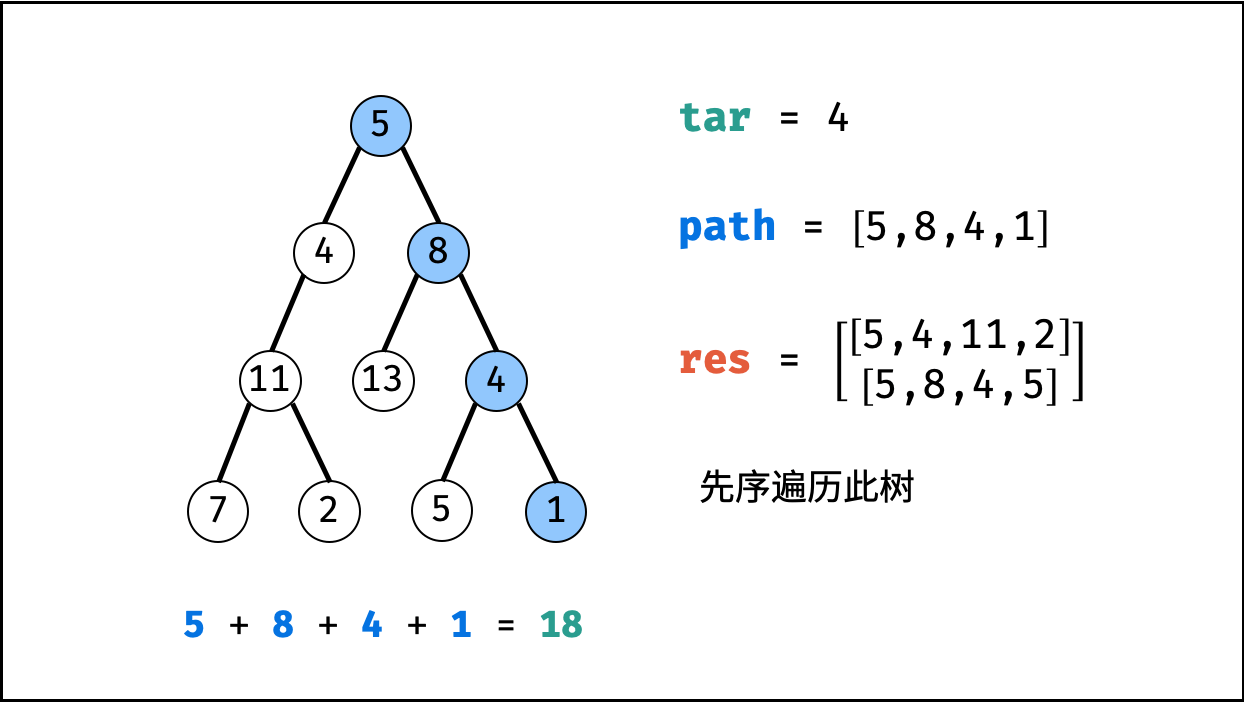
利用回溯+深度优先搜索即可解决。
这样要重点注意的是:回溯时,前进和后退要成对出现。
| 非常典型的回溯问题! |
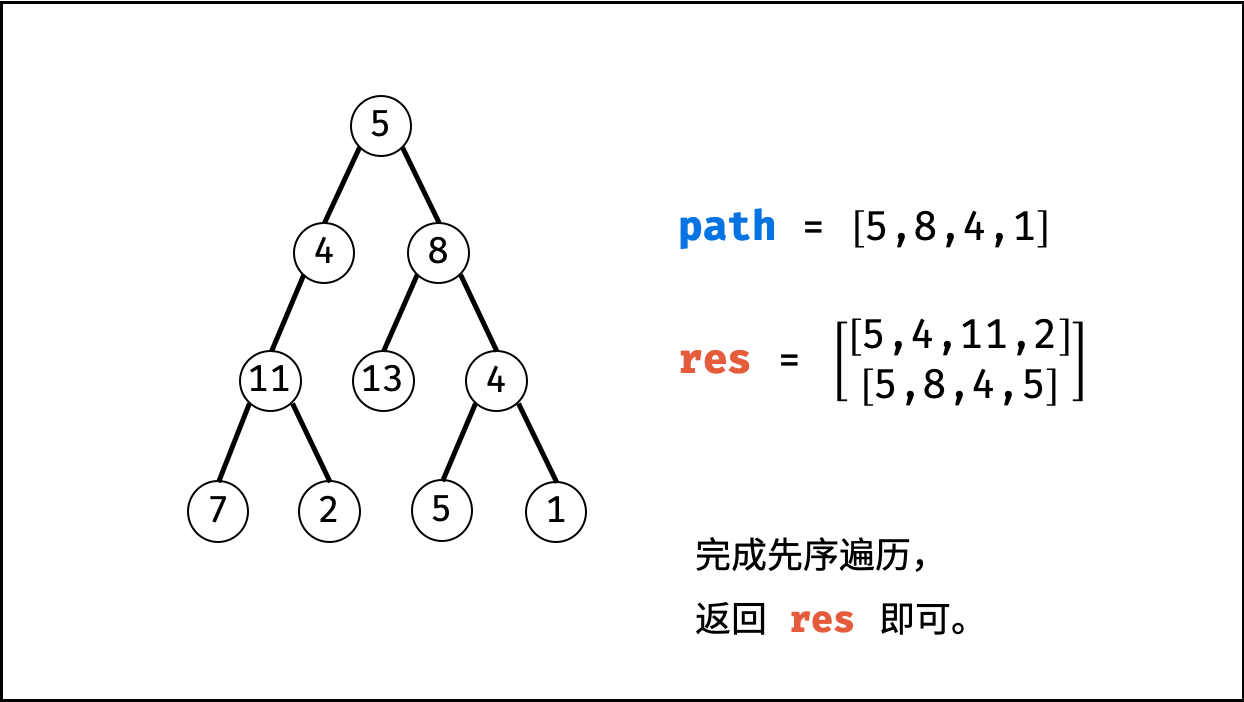
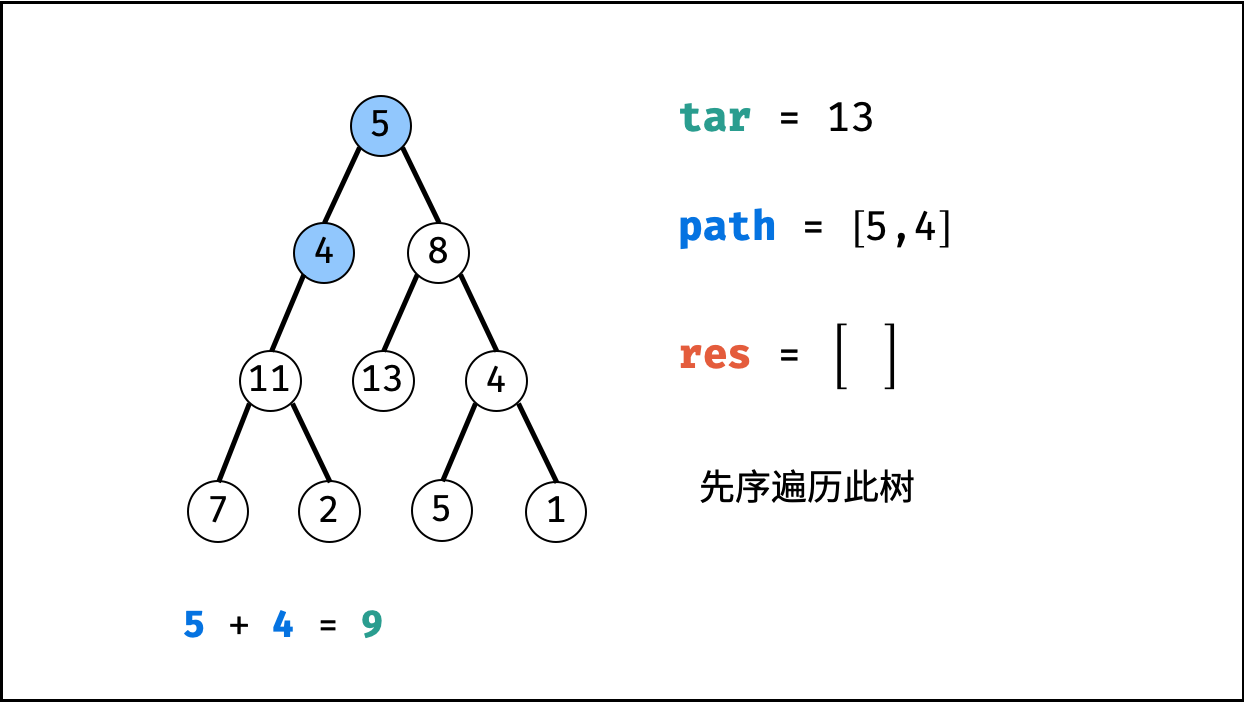
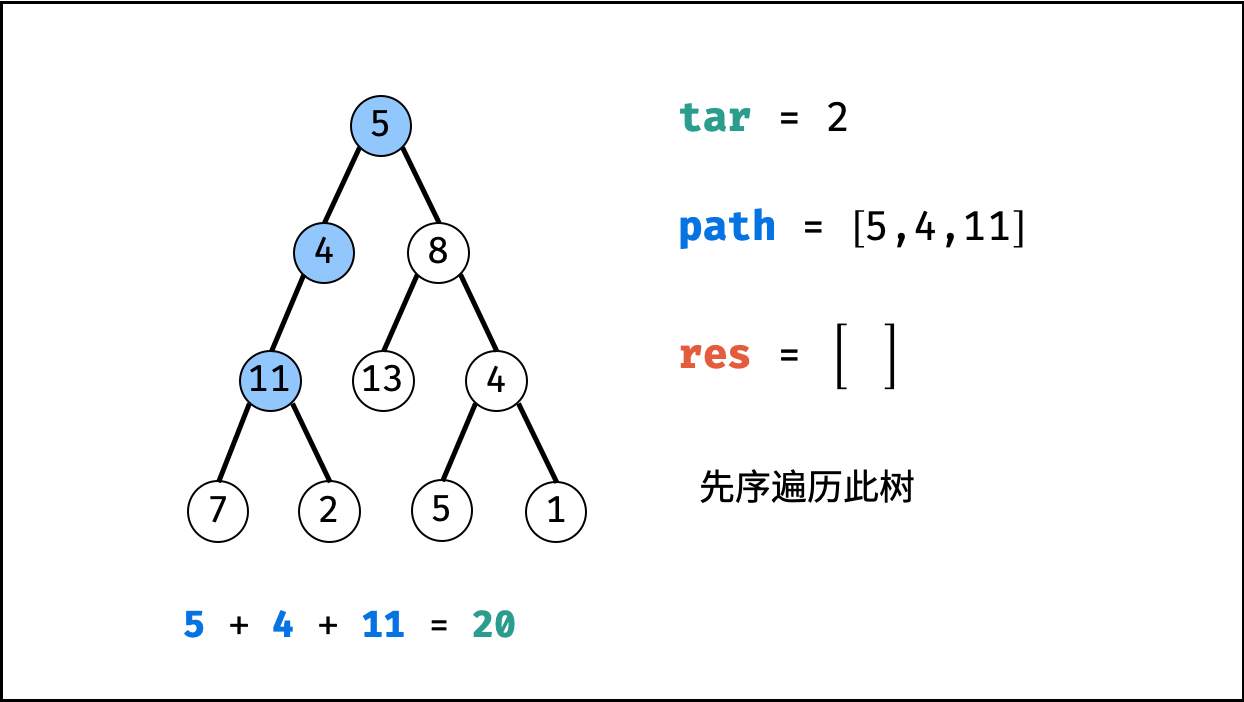
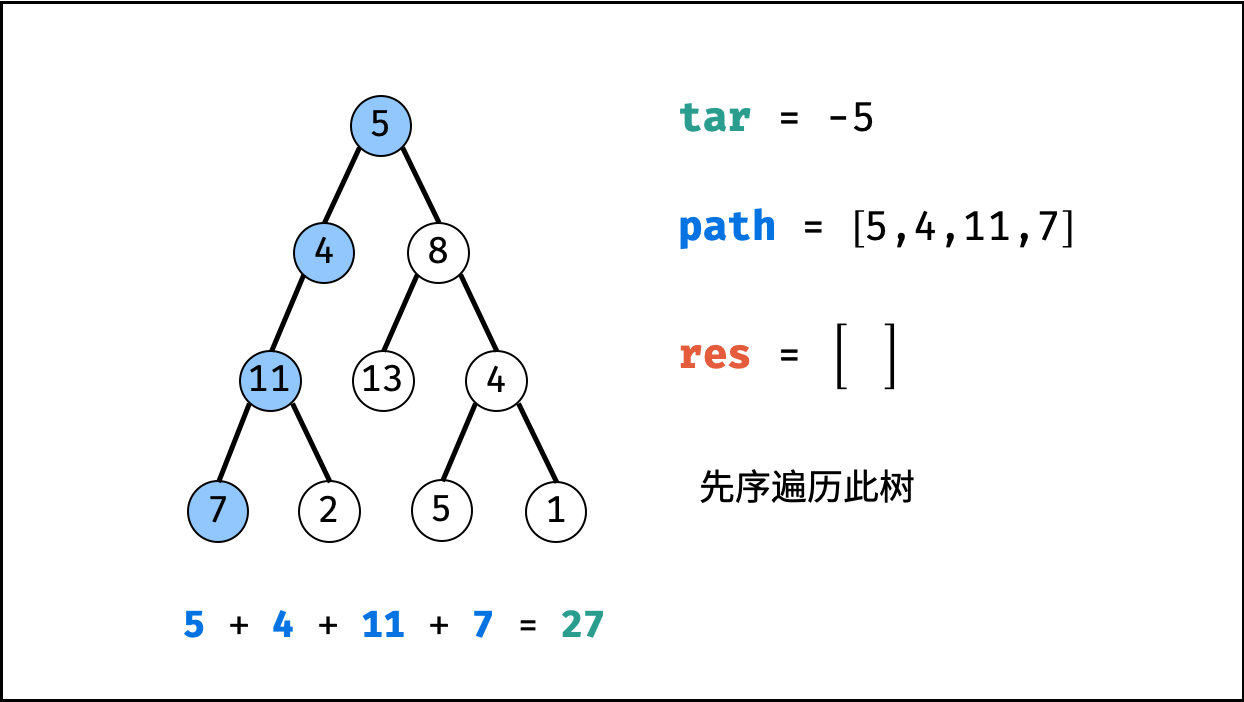
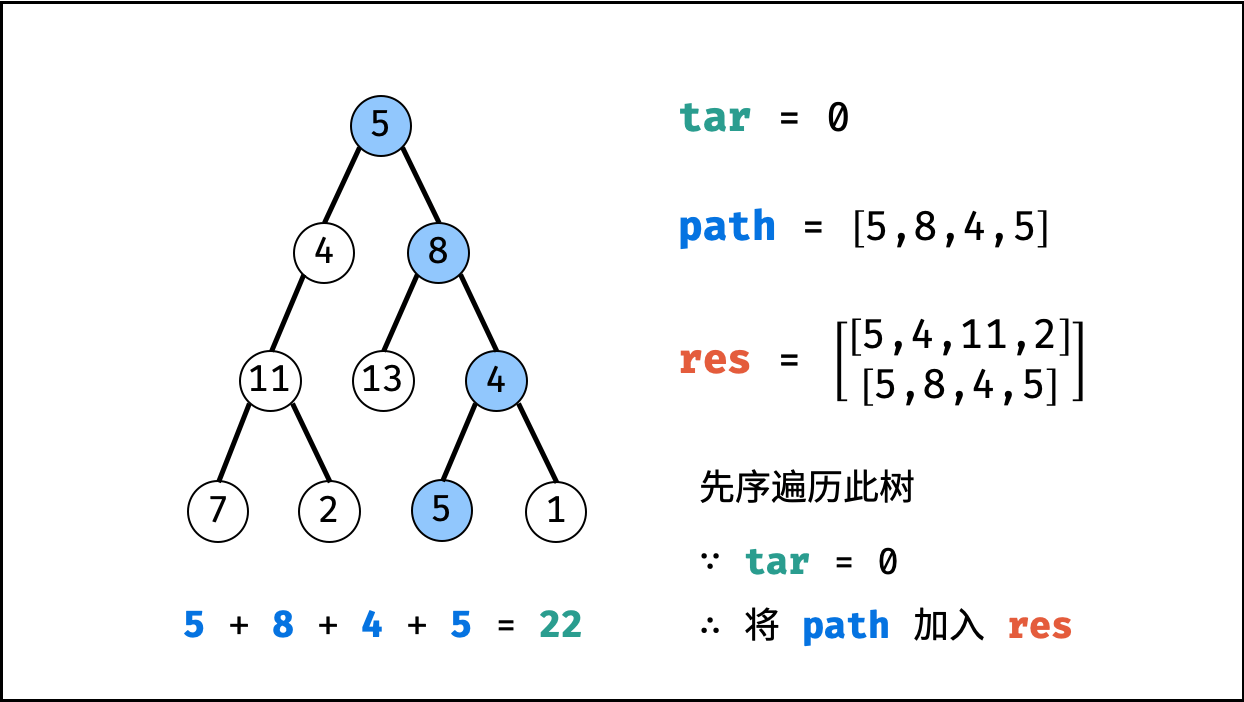
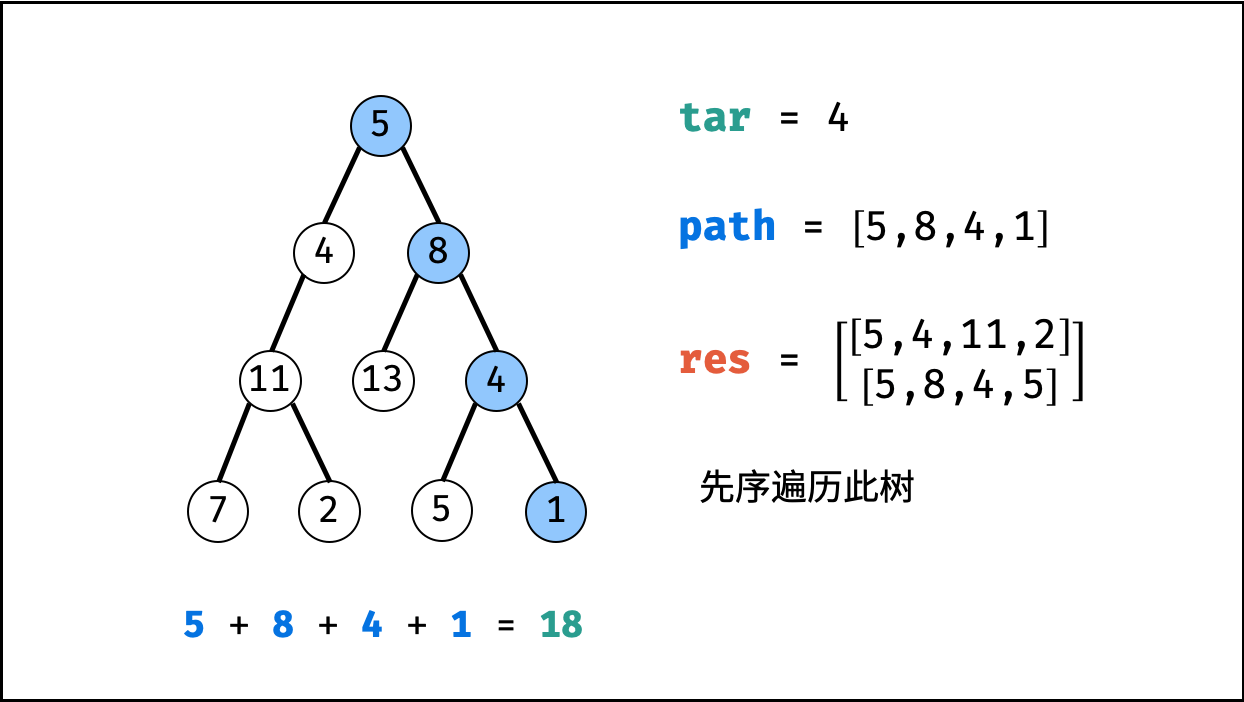
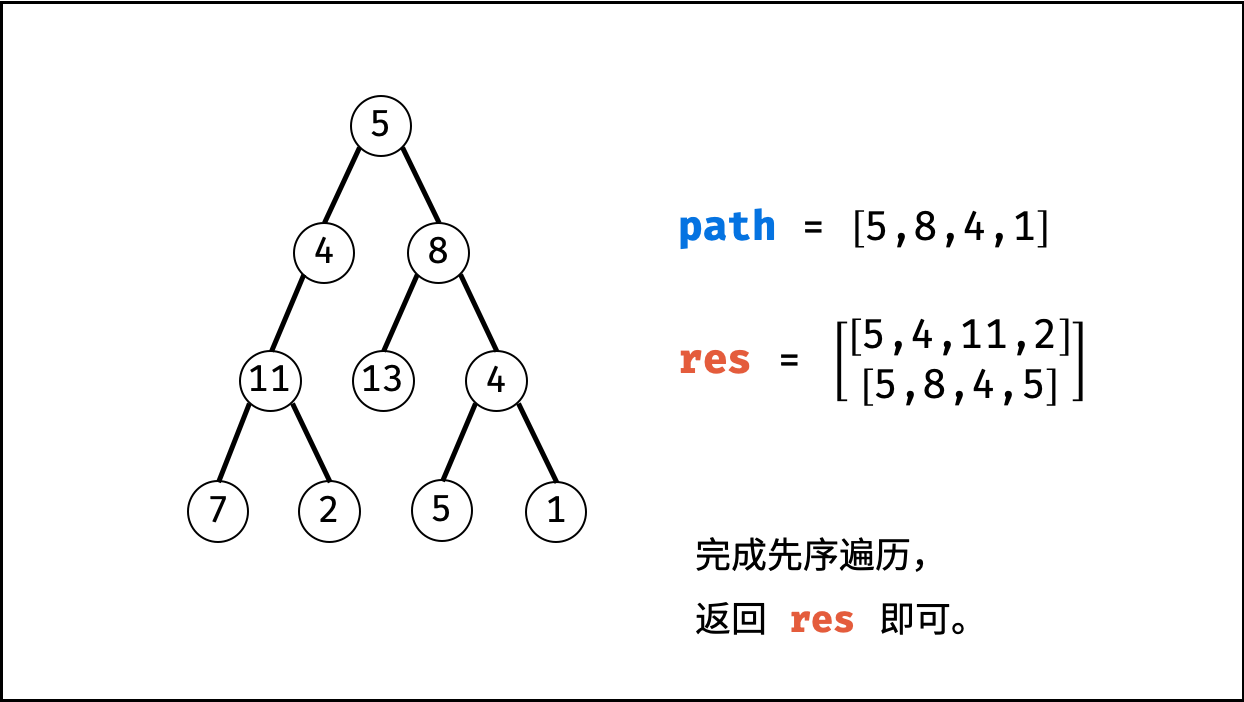
-
一刷
-
二刷(待优化)
-
二刷(优化)
-
三刷
-
四刷
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
/**
* Runtime: 1 ms, faster than 100.00% of Java online submissions for Path Sum II.
* Memory Usage: 41.8 MB, less than 6.06% of Java online submissions for Path Sum II.
*/
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new LinkedList<>();
dfs(root, sum, result, new ArrayDeque<>());
return result;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int sum, List<List<Integer>> result, Deque<Integer> current) {
if (Objects.isNull(root)) {
return;
}
sum -= root.val;
current.addLast(root.val);
if (sum == 0 && Objects.isNull(root.left) && Objects.isNull(root.right)) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(current));
}
dfs(root.left, sum, result, current);
dfs(root.right, sum, result, current);
current.removeLast();
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
/**
* 原始解法
*
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2024-06-20 18:48
*/
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
pathSum(root, sum, result, new ArrayList<>());
return result;
}
private void pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum, List<List<Integer>> result, List<Integer> path) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
int nextSum = sum - root.val;
if (nextSum == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null) {
path.add(root.val);
result.add(path);
} else {
// 这里每次都需要创建 List 对象,可以优化一下
ArrayList<Integer> lp = new ArrayList<>(path);
lp.add(root.val);
pathSum(root.left, nextSum, result, lp);
// 这里每次都需要创建 List 对象,可以优化一下
ArrayList<Integer> rp = new ArrayList<>(path);
rp.add(root.val);
pathSum(root.right, nextSum, result, rp);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
/**
* 原始解法
*
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2020-02-07 22:31
*/
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
pathSum(root, sum, result, path);
return result;
}
private void pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum, List<List<Integer>> result, Deque<Integer> path) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
int nextSum = sum - root.val;
// 用前添加
path.addLast(root.val);
if (nextSum == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
pathSum(root.left, nextSum, result, path);
pathSum(root.right, nextSum, result, path);
// 用完删除,这不就是回溯吗?
path.removeLast();
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2024-06-20 18:48
*/
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
backtrack(root, targetSum, result, path);
return result;
}
private void backtrack(TreeNode root, int targetSum,
List<List<Integer>> result, List<Integer> path) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
int nextSum = targetSum - root.val;
path.add(root.val);
if (nextSum == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null) {
result.add(new ArrayList(path));
}
backtrack(root.left, nextSum, result, path);
backtrack(root.right, nextSum, result, path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2025-09-25 22:46:05
*/
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
backtrack(root, targetSum, result, path);
return result;
}
private void backtrack(TreeNode root, int targetSum,
List<List<Integer>> result,
List<Integer> path) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
path.add(root.val);
int nextTarget = targetSum - root.val;
if (nextTarget == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
backtrack(root.left, nextTarget, result, path);
backtrack(root.right, nextTarget, result, path);
path.removeLast();
}