友情支持
如果您觉得这个笔记对您有所帮助,看在D瓜哥码这么多字的辛苦上,请友情支持一下,D瓜哥感激不尽,😜
|
|
有些打赏的朋友希望可以加个好友,欢迎关注D 瓜哥的微信公众号,这样就可以通过公众号的回复直接给我发信息。

公众号的微信号是: jikerizhi。因为众所周知的原因,有时图片加载不出来。 如果图片加载不出来可以直接通过搜索微信号来查找我的公众号。 |
133. 克隆图
图中的每个节点都包含它的值 val(int)和其邻居的列表(list[Node])。
1
2
3
4
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
测试用例格式:
简单起见,每个节点的值都和它的索引相同。例如,第一个节点值为 1(val = 1),第二个节点值为 2(val = 2),以此类推。该图在测试用例中使用邻接列表表示。
邻接列表 是用于表示有限图的无序列表的集合。每个列表都描述了图中节点的邻居集。
给定节点将始终是图中的第一个节点(值为 1)。你必须将 给定节点的拷贝 作为对克隆图的引用返回。
示例 1:
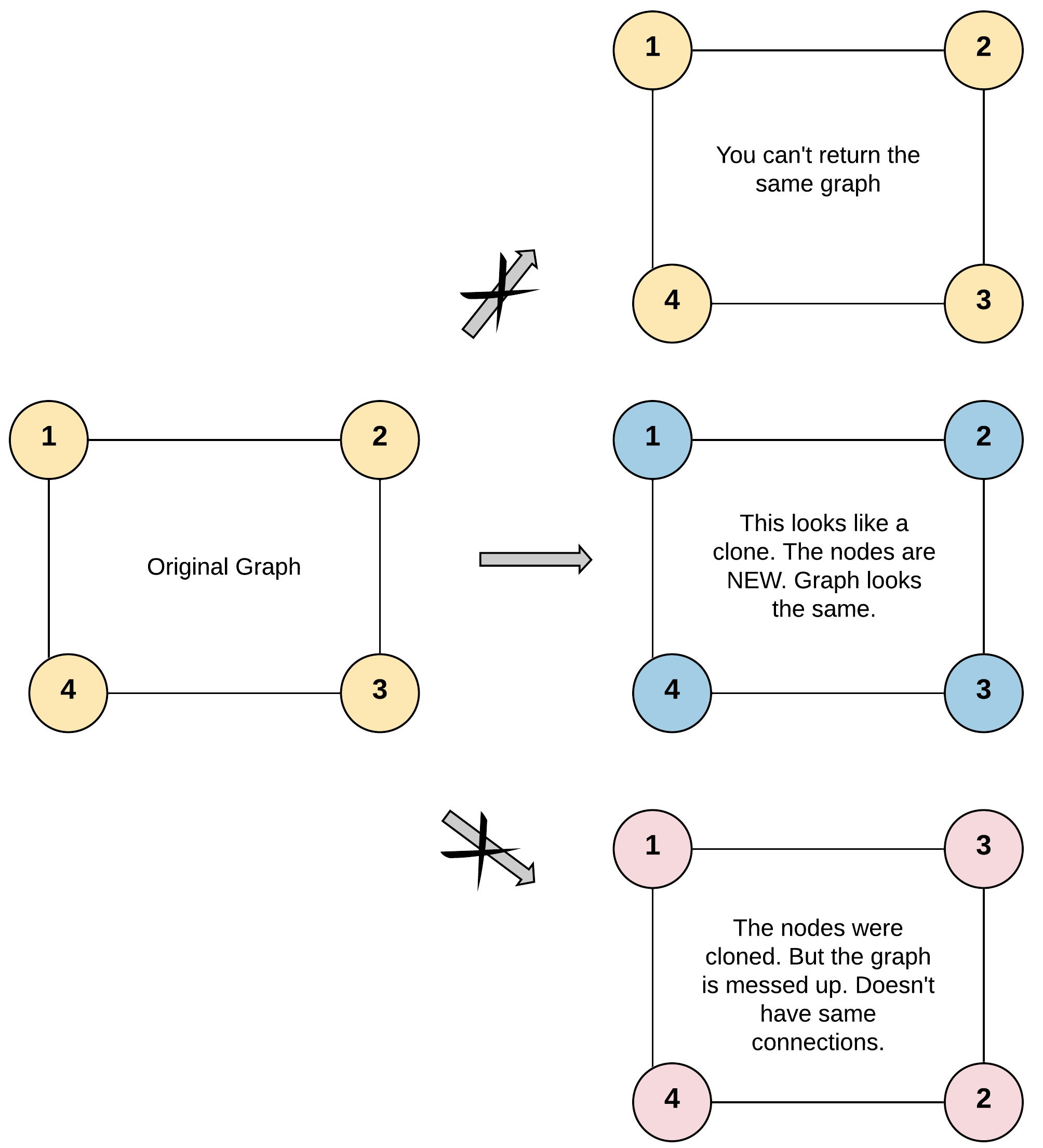
输入:adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] 输出:[[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] 解释: 图中有 4 个节点。 节点 1 的值是 1,它有两个邻居:节点 2 和 4 。 节点 2 的值是 2,它有两个邻居:节点 1 和 3 。 节点 3 的值是 3,它有两个邻居:节点 2 和 4 。 节点 4 的值是 4,它有两个邻居:节点 1 和 3 。
示例 2:
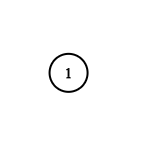
输入:adjList = [[]] 输出:[[]] 解释:输入包含一个空列表。该图仅仅只有一个值为 1 的节点,它没有任何邻居。
示例 3:
输入:adjList = [] 输出:[] 解释:这个图是空的,它不含任何节点。
提示:
-
这张图中的节点数在
[0, 100]之间。 -
1 <= Node.val <= 100 -
每个节点值
Node.val都是唯一的, -
图中没有重复的边,也没有自环。
-
图是连通图,你可以从给定节点访问到所有节点。
思路分析
这道题可以使用类似 138. 随机链表的复制 的解法来求解。
-
一刷
-
二刷
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2020-02-10 00:22
*/
// Definition for a Node.
static class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
public Node() {
val = 0;
neighbors = new ArrayList<>();
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
neighbors = new ArrayList<>();
}
public Node(int _val, ArrayList<Node> _neighbors) {
val = _val;
neighbors = _neighbors;
}
}
/**
* Runtime: 28 ms, faster than 34.86% of Java online submissions for Clone Graph.
* Memory Usage: 38.8 MB, less than 5.88% of Java online submissions for Clone Graph.
*/
public Node cloneGraphDfs(Node node) {
Map<Node, Node> dict = new HashMap<>();
return dfs(node, dict);
}
private Node dfs(Node node, Map<Node, Node> dict) {
if (Objects.isNull(node)) {
return null;
}
if (dict.containsKey(node)) {
return dict.get(node);
}
Node clone = new Node(node.val, new ArrayList<>(node.neighbors.size()));
dict.put(node, clone);
for (Node n : node.neighbors) {
clone.neighbors.add(dfs(n, dict));
}
return clone;
}
/**
* Runtime: 26 ms, faster than 47.60% of Java online submissions for Clone Graph.
* Memory Usage: 39.3 MB, less than 5.88% of Java online submissions for Clone Graph.
*/
public Node cloneGraph(Node node) {
if (Objects.isNull(node)) {
return null;
}
Map<Node, Node> dict = new HashMap<>();
dict.put(node, new Node(node.val, new ArrayList<>(node.neighbors.size())));
Deque<Node> deque = new LinkedList<>();
deque.addLast(node);
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
Node curr = deque.removeFirst();
for (Node n : curr.neighbors) {
if (!dict.containsKey(n)) {
dict.put(n, new Node(n.val, new ArrayList<>(n.neighbors.size())));
deque.addLast(n);
}
dict.get(curr).neighbors.add(dict.get(n));
}
}
return dict.get(node);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2025-06-05 09:36:00
*/
public Node cloneGraph(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
return dfs(node, map);
}
private Node dfs(Node node, Map<Node, Node> map) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
if (map.containsKey(node)) {
return map.get(node);
}
Node newNode = new Node(node.val);
map.put(node, newNode);
for (Node neighbor : node.neighbors) {
newNode.neighbors.add(dfs(neighbor, map));
}
return newNode;
}