友情支持
如果您觉得这个笔记对您有所帮助,看在D瓜哥码这么多字的辛苦上,请友情支持一下,D瓜哥感激不尽,😜
|
|
有些打赏的朋友希望可以加个好友,欢迎关注D 瓜哥的微信公众号,这样就可以通过公众号的回复直接给我发信息。

公众号的微信号是: jikerizhi。因为众所周知的原因,有时图片加载不出来。 如果图片加载不出来可以直接通过搜索微信号来查找我的公众号。 |
96. 不同的二叉搜索树
给你一个整数 n ,求恰由 n 个节点组成且节点值从 1 到 n 互不相同的 二叉搜索树 有多少种?返回满足题意的二叉搜索树的种数。
示例 1:
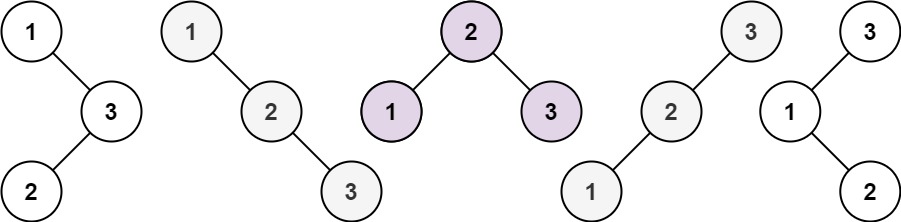
输入:n = 3 输出:5
示例 2:
输入:n = 1 输出:1
提示:
-
1 <= n <= 19
思路分析
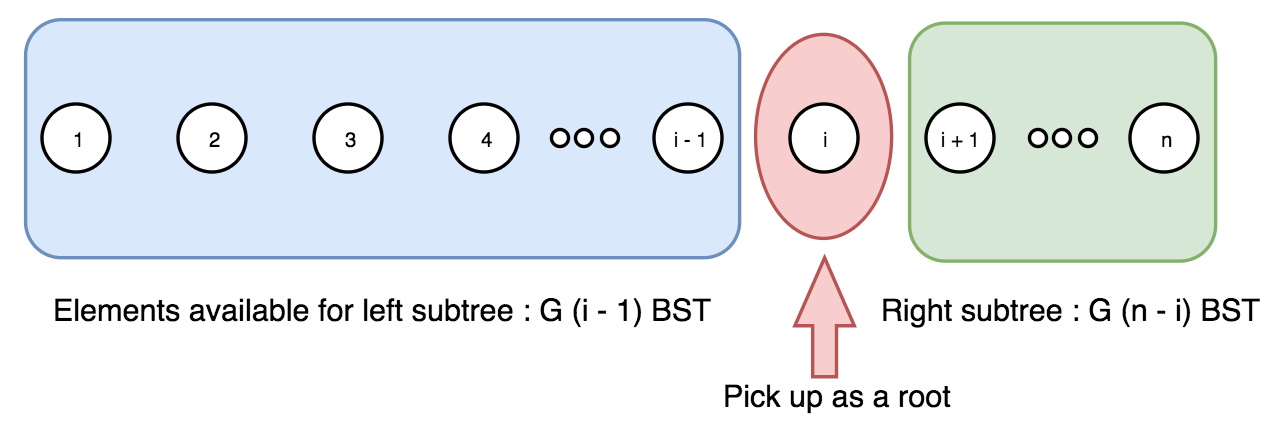
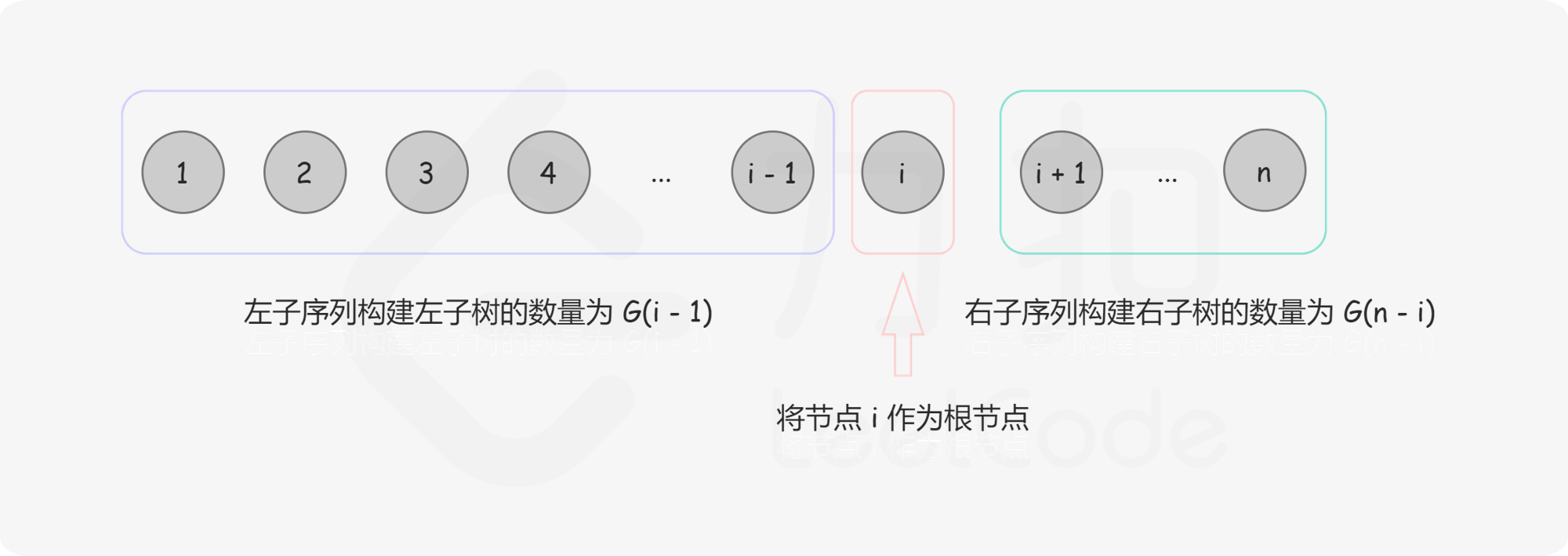
给定一个有序序列 1 … n,为了根据序列构建一棵二叉搜索树。我们可以遍历每个数字 i,将该数字作为树根,1 … (i-1) 序列将成为左子树,(i+1) … n 序列将成为右子树。于是,我们可以递归地从子序列构建子树。
在上述方法中,由于根各自不同,每棵二叉树都保证是独特的。
可见,问题可以分解成规模较小的子问题。因此,我们可以存储并复用子问题的解,而不是递归的(也重复的)解决这些子问题,这就是动态规划法。
给定序列 1 … n,我们选出数字 i 作为根,则对于根 i 的不同二叉搜索树数量 \(F(i, n)\),是左右子树个数的笛卡尔积,如下图所示:
公式推到过程
\$G_{(n)} \text { 长度为 n 的序列能构成的不同二叉搜索树的个数 }\$
\$F_{(i, n)} \text { 以 i 为根、序列长度为 n 的不同二叉搜索树个数 (1≤i≤n)。 }\$
\$G_{n}=\sum_{i=1}^{n} F_{(i, n)} = F_{(1, n)} + F_{(2, n)} + ... + F_{(n-1, n)} + F_{(n, n)}\$
\$F_{(i, n)} = G_{(i-1)} \cdot G_{(n-i)}\$
\$G_{(n)} = \sum_{i=1}^n G_{(i-1)} \cdot G_{(n-i)} = G_{0} \cdot G_{(n-1)} + ... + G_{(n-1)} \cdot G_{0}\$
\$C_{n+1}=\frac{2(2 n+1)}{n+2} C_{n} \text { 明安图数 或 卡特兰数}\$
\$F_{(i, n)} \text { 以 i 为根、序列长度为 n 的不同二叉搜索树个数 (1≤i≤n)。 }\$
\$G_{n}=\sum_{i=1}^{n} F_{(i, n)} = F_{(1, n)} + F_{(2, n)} + ... + F_{(n-1, n)} + F_{(n, n)}\$
\$F_{(i, n)} = G_{(i-1)} \cdot G_{(n-i)}\$
\$G_{(n)} = \sum_{i=1}^n G_{(i-1)} \cdot G_{(n-i)} = G_{0} \cdot G_{(n-1)} + ... + G_{(n-1)} \cdot G_{0}\$
\$C_{n+1}=\frac{2(2 n+1)}{n+2} C_{n} \text { 明安图数 或 卡特兰数}\$
| 注意:题目要是二叉搜索树! |
没想到这里还埋了一个数学知识:Catalan number:
\$C_{0}=1 \quad \text { and } \quad C_{n+1}=\sum_{i=0}^{n} C_{i} C_{n-i} \quad \text { for } n \geq 0\$
\$C_{0}=1 \text { and } C_{1}=1\$
\$C_{n}=\sum_{i=1}^{n} C_{i-1} C_{n-i} \quad\$
\$C_{0}=1, \quad C_{n+1}=\frac{2(2 n+1)}{n+2} C_{n}\$
\$C_{0}=1 \text { and } C_{1}=1\$
\$C_{n}=\sum_{i=1}^{n} C_{i-1} C_{n-i} \quad\$
\$C_{0}=1, \quad C_{n+1}=\frac{2(2 n+1)}{n+2} C_{n}\$
附加题:参考资料显示,关于 Catalan number 有好多好玩的东西可以把玩。查资料把玩把玩。
-
一刷
-
二刷
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
/**
* Runtime: 0 ms, faster than 100.00% of Java online submissions for Unique Binary Search Trees.
* Memory Usage: 38.2 MB, less than 5.55% of Java online submissions for Unique Binary Search Trees.
*
* Copy from: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees/solution/bu-tong-de-er-cha-sou-suo-shu-by-leetcode/[不同的二叉搜索树 - 不同的二叉搜索树 - 力扣(LeetCode)]
*
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2020-01-27 22:14
*/
public int numTreesCatalanNumber(int n) {
long C = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
C = C * 2 * (2 * i + 1) / (i + 2);
}
return (int) C;
}
/**
* Runtime: 0 ms, faster than 100.00% of Java online submissions for Unique Binary Search Trees.
* Memory Usage: 36 MB, less than 5.55% of Java online submissions for Unique Binary Search Trees.
*
* Copy from: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees/solution/bu-tong-de-er-cha-sou-suo-shu-by-leetcode/[不同的二叉搜索树 - 不同的二叉搜索树 - 力扣(LeetCode)]
*/
public int numTrees(int n) {
int[] g = new int[n + 1];
g[0] = 1;
g[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
g[i] += g[j - 1] * g[i - j];
}
}
return g[n];
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2020-01-27 22:14
*/
public int numTrees(int num) {
int[] r = new int[num + 1];
r[0] = 1;
r[1] = 1;
for (int n = 2; n <= num; n++) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
r[n] += r[i - 1] * r[n - i];
}
}
return r[num];
}