友情支持
如果您觉得这个笔记对您有所帮助,看在D瓜哥码这么多字的辛苦上,请友情支持一下,D瓜哥感激不尽,😜
|
|
有些打赏的朋友希望可以加个好友,欢迎关注D 瓜哥的微信公众号,这样就可以通过公众号的回复直接给我发信息。

公众号的微信号是: jikerizhi。因为众所周知的原因,有时图片加载不出来。 如果图片加载不出来可以直接通过搜索微信号来查找我的公众号。 |
30. 串联所有单词的子串
给定一个字符串 s 和一个字符串数组 words。words 中所有字符串 长度相同。
s 中的 串联子串 是指一个包含 words 中所有字符串以任意顺序排列连接起来的子串。
-
例如,如果
words = ["ab","cd","ef"],那么"abcdef","abefcd","cdabef","cdefab","efabcd",和"efcdab"都是串联子串。"acdbef"不是串联子串,因为他不是任何words排列的连接。
返回所有串联子串在 s 中的开始索引。你可以以 任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:s = "barfoothefoobarman", words = ["foo","bar"] 输出:[0,9] 解释:因为 words.length == 2 同时 words[i].length == 3,连接的子字符串的长度必须为 6。 子串 "barfoo" 开始位置是 0。它是 words 中以 ["bar","foo"] 顺序排列的连接。 子串 "foobar" 开始位置是 9。它是 words 中以 ["foo","bar"] 顺序排列的连接。 输出顺序无关紧要。返回 [9,0] 也是可以的。
示例 2:
输入:s = "wordgoodgoodgoodbestword", words = ["word","good","best","word"] 输出:[] 解释:因为 words.length == 4 并且 words[i].length == 4,所以串联子串的长度必须为 16。 s 中没有子串长度为 16 并且等于 words 的任何顺序排列的连接。 所以我们返回一个空数组。
示例 3:
输入:s = "barfoofoobarthefoobarman", words = ["bar","foo","the"] 输出:[6,9,12] 解释:因为 words.length == 3 并且 words[i].length == 3,所以串联子串的长度必须为 9。 子串 "foobarthe" 开始位置是 6。它是 words 中以 ["foo","bar","the"] 顺序排列的连接。 子串 "barthefoo" 开始位置是 9。它是 words 中以 ["bar","the","foo"] 顺序排列的连接。 子串 "thefoobar" 开始位置是 12。它是 words 中以 ["the","foo","bar"] 顺序排列的连接。
提示:
-
1 <= s.length <= 104 -
1 <= words.length <= 5000 -
1 <= words[i].length <= 30 -
words[i]和s由小写英文字母组成
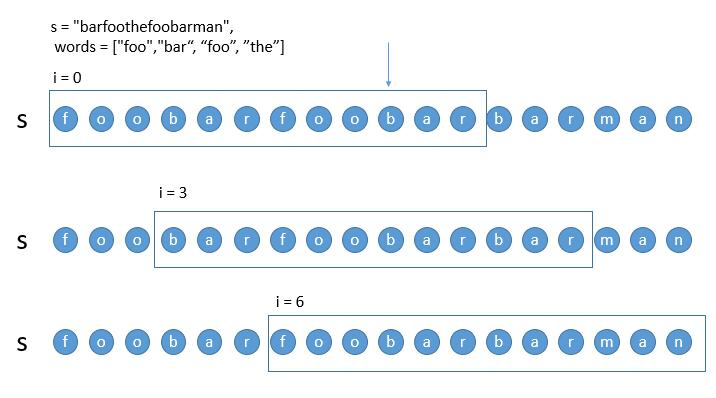
思路分析
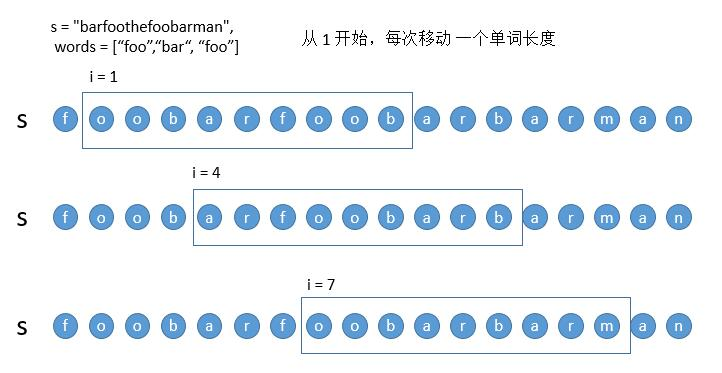
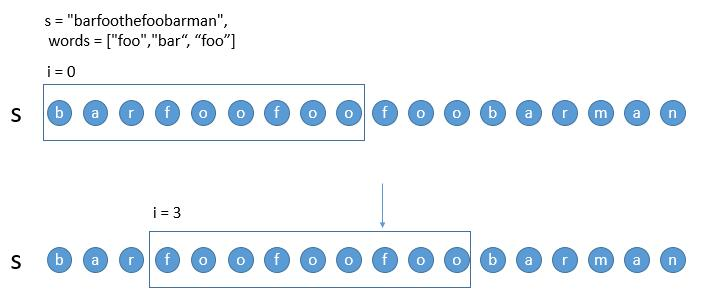
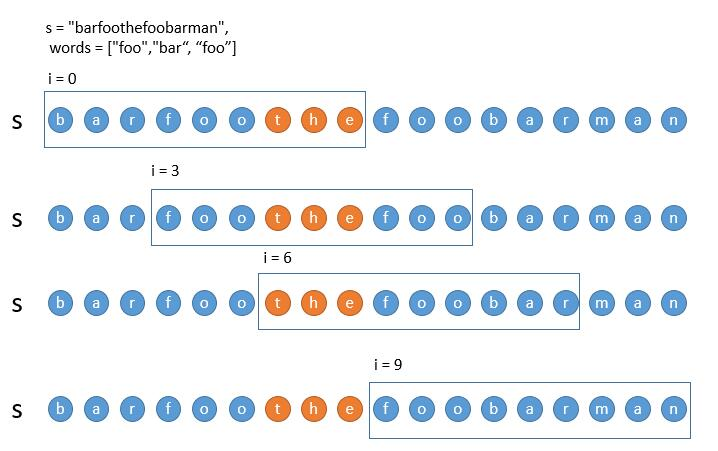
滑动窗口。需要按照如下三种情况处理窗口
-
遇到了完全符合的子串
-
遇到了不在字典里的子串
-
单词数量超过了字典中的单词数量
-
一刷
-
二刷
-
二刷
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2025-04-23 14:35:27
*/
public List<Integer> findSubstring(String s, String[] words) {
Map<String, Integer> dict = new HashMap<>();
for (String word : words) {
dict.put(word, dict.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);
}
int wordLen = words[0].length();
int wordNum = words.length;
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < wordLen; i++) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int left = i, right = i, hit = 0;
while (right + wordLen <= s.length()) {
String word = s.substring(right, right + wordLen);
right += wordLen;
if (dict.containsKey(word)) {
int num = map.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1;
map.put(word, num);
hit++;
// 出现情况三,遇到了符合的单词,但是次数超了
if (num > dict.get(word)) {
// 一直移除单词,直到次数符合
while (map.get(word) > dict.get(word)) {
String deleteWord = s.substring(left, left + wordLen);
map.compute(deleteWord, (k, cnt) -> cnt - 1);
left += wordLen;
hit--;
}
}
} else {
// 出现情况二,遇到了不匹配的单词,直接将 left 移动到该单词的后边
map.clear();
hit = 0;
left = right;
}
if (hit == wordNum) {
result.add(left);
// 出现情况一,子串完全匹配,我们将上一个子串的第一个单词从tmp中移除,窗口后移wordLen
String firstWord = s.substring(left, left + wordLen);
map.compute(firstWord, (k, cnt) -> cnt - 1);
hit--;
left += wordLen;
}
}
}
return result;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
/**
* 超时(152/182)
*
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2026-01-06 20:13:53
*/
public List<Integer> findSubstring(String s, String[] words) {
if (s.length() < words.length * words[0].length()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
int[] sc = new int[26];
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
sc[c - 'a']++;
}
for (String word : words) {
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
sc[c - 'a']--;
if (sc[c - 'a'] < 0) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}
}
for (String word : words) {
if (!s.contains(word)) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}
Set<String> permutations = new HashSet<>();
StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder();
boolean[] used = new boolean[words.length];
buildPermutations(words, permutations, path, used);
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(permutations.size());
for (String p : permutations) {
result.addAll(findAll(s, p, 0));
}
return result;
}
private List<Integer> findAll(String s, String p, int index) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
while (index + p.length() <= s.length()) {
int i = s.indexOf(p, index);
if (i < 0) {
return result;
}
result.add(i);
index = i + 1;
}
return result;
}
private void buildPermutations(String[] words, Set<String> permutations,
StringBuilder path, boolean[] used) {
if (path.length() == words.length * words[0].length()) {
permutations.add(path.toString());
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
if (used[i]) {
continue;
}
String word = words[i];
path.append(word);
used[i] = true;
buildPermutations(words, permutations, path, used);
used[i] = false;
path.delete(path.length() - word.length(), path.length());
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2026-01-06 20:50:00
*/
public List<Integer> findSubstring(String s, String[] words) {
int wordLength = words[0].length(); // 单词长度
int windowLength = wordLength * words.length; // 所有单词的总长度,即窗口大小
// 目标:窗口中的单词出现次数必须与 dict 完全一致
Map<String, Integer> dict = new HashMap<>();
for (String word : words) {
dict.merge(word, 1, Integer::sum);
}
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
// 枚举第一个窗口的左端点,做 wordLen 次起点不同的滑动窗口
for (int start = 0; start < wordLength; start++) {
Map<String, Integer> counter = new HashMap<>();
int overload = 0; // 统计过多的单词个数(包括不在 words 中的单词)
// 枚举窗口最后一个单词的右开端点
for (int right = start + wordLength; right <= s.length(); right += wordLength) {
// 1. inWord 进入窗口
String inWord = s.substring(right - wordLength, right);
// 下面 cnt[inWord]++ 后,inWord 的出现次数过多
if (counter.getOrDefault(inWord, 0).equals(dict.getOrDefault(inWord, 0))) {
overload++;
}
counter.merge(inWord, 1, Integer::sum); // cnt[inWord]++
int left = right - windowLength; // 窗口第一个单词的左端点
// 窗口大小不足 windowLen
if (left < 0) {
continue;
}
// 2. 更新答案
// 如果没有超出 dict 的单词,那么也不会有少于 dict 的单词
if (overload == 0) {
result.add(left);
}
// 3. 窗口最左边的单词 outWord 离开窗口,为下一轮循环做准备
String outWord = s.substring(left, left + wordLength);
counter.merge(outWord, -1, Integer::sum); // cnt[outWord]--
if (counter.get(outWord).equals(dict.getOrDefault(outWord, 0))) {
overload--;
}
}
}
return result;
}