友情支持
如果您觉得这个笔记对您有所帮助,看在D瓜哥码这么多字的辛苦上,请友情支持一下,D瓜哥感激不尽,😜
|
|
有些打赏的朋友希望可以加个好友,欢迎关注D 瓜哥的微信公众号,这样就可以通过公众号的回复直接给我发信息。

公众号的微信号是: jikerizhi。因为众所周知的原因,有时图片加载不出来。 如果图片加载不出来可以直接通过搜索微信号来查找我的公众号。 |
173. 二叉搜索树迭代器
实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器类 BSTIterator,表示一个按中序遍历二叉搜索树(BST)的迭代器:
-
BSTIterator(TreeNode root)初始化BSTIterator类的一个对象。BST 的根节点root会作为构造函数的一部分给出。指针应初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,且该数字小于 BST 中的任何元素。 -
boolean hasNext()如果向指针右侧遍历存在数字,则返回true;否则返回false。 -
`int next()`将指针向右移动,然后返回指针处的数字。
注意,指针初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,所以对 next() 的首次调用将返回 BST 中的最小元素。
你可以假设 next() 调用总是有效的,也就是说,当调用 next() 时,BST 的中序遍历中至少存在一个下一个数字。
示例:
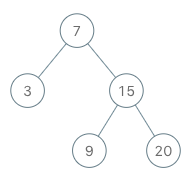
输入 ["BSTIterator", "next", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext"] [[[7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []] 输出 [null, 3, 7, true, 9, true, 15, true, 20, false] 解释 BSTIterator bSTIterator = new BSTIterator([7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]); bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 3 bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 7 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 9 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 15 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 20 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 False
提示:
-
树中节点的数目在范围
[1, 105]内 -
0 <= Node.val <= 106 -
最多调用
105次hasNext和next操作
进阶:
-
你可以设计一个满足下述条件的解决方案吗?
next()和hasNext()操作均摊时间复杂度为O(1),并使用 \(O(h)\) 内存。其中h是树的高度。
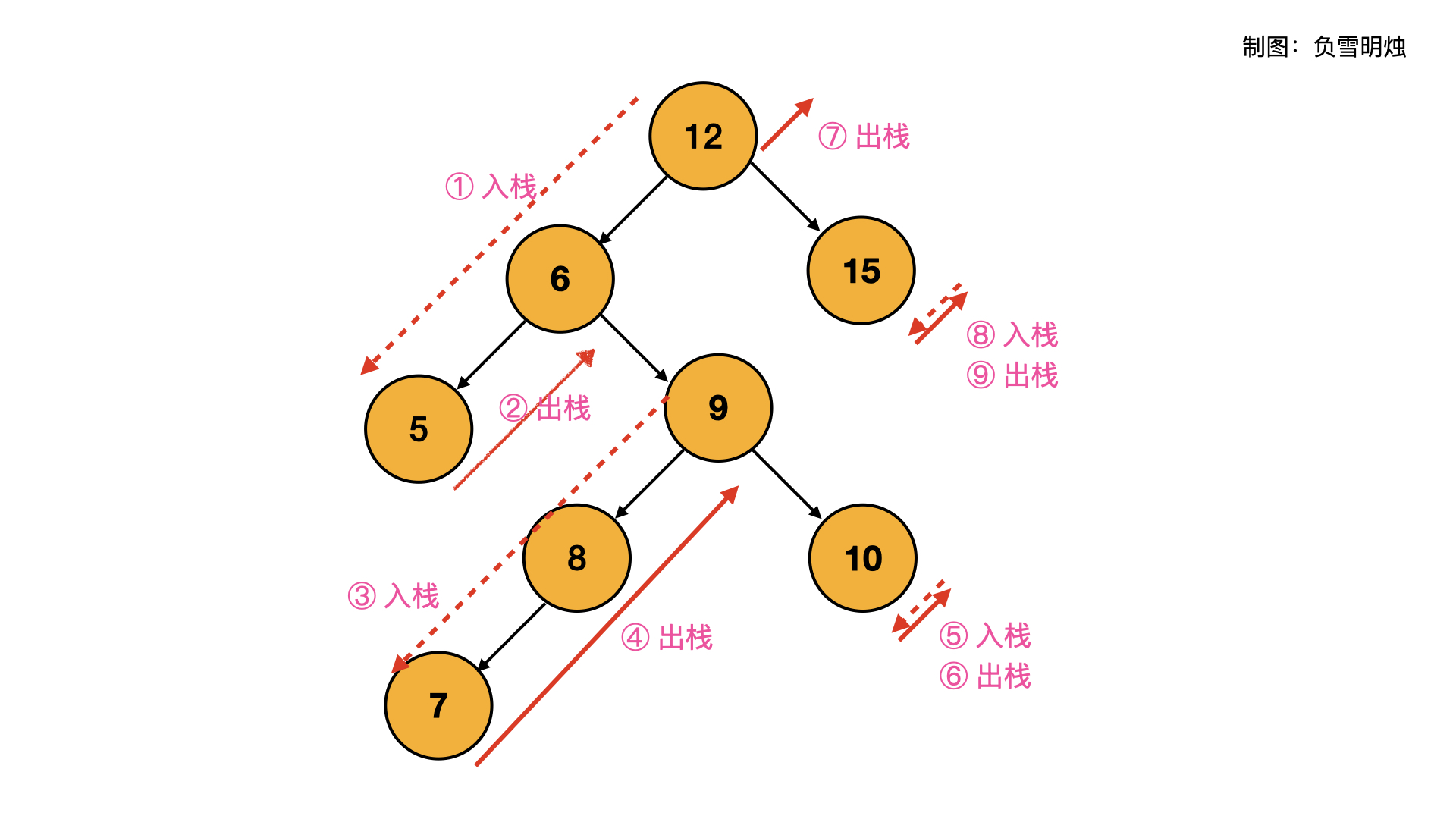
思路分析
使用栈模拟递归调用。
-
一刷
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2025-06-10 20:13:13
*/
class BSTIterator {
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
}
public int next() {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
TreeNode curr = node.right;
while (curr != null) {
stack.push(curr);
curr = curr.left;
}
return node.val;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return !stack.isEmpty();
}
}