友情支持
如果您觉得这个笔记对您有所帮助,看在D瓜哥码这么多字的辛苦上,请友情支持一下,D瓜哥感激不尽,😜
|
|
有些打赏的朋友希望可以加个好友,欢迎关注D 瓜哥的微信公众号,这样就可以通过公众号的回复直接给我发信息。

公众号的微信号是: jikerizhi。因为众所周知的原因,有时图片加载不出来。 如果图片加载不出来可以直接通过搜索微信号来查找我的公众号。 |
365. 水壶问题
有两个水壶,容量分别为 x 和 y 升。水的供应是无限的。确定是否有可能使用这两个壶准确得到 target 升。
你可以:
-
装满任意一个水壶
-
清空任意一个水壶
-
将水从一个水壶倒入另一个水壶,直到接水壶已满,或倒水壶已空。
示例 1:
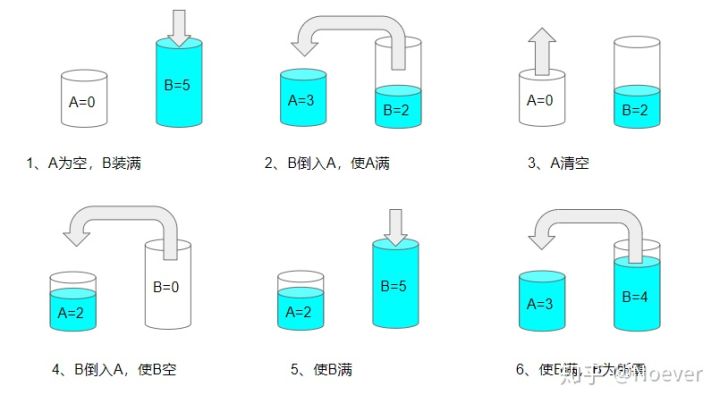
输入: x = 3,y = 5,target = 4 输出: true 解释: 按照以下步骤操作,以达到总共 4 升水: 1. 装满 5 升的水壶(0, 5)。 2. 把 5 升的水壶倒进 3 升的水壶,留下 2 升(3, 2)。 3. 倒空 3 升的水壶(0, 2)。 4. 把 2 升水从 5 升的水壶转移到 3 升的水壶(2, 0)。 5. 再次加满 5 升的水壶(2, 5)。 6. 从 5 升的水壶向 3 升的水壶倒水直到 3 升的水壶倒满。5 升的水壶里留下了 4 升水(3, 4)。 7. 倒空 3 升的水壶。现在,5 升的水壶里正好有 4 升水(0, 4)。 参考:来自著名的 "Die Hard"
示例 2:
输入: x = 2, y = 6, target = 5 输出: false
示例 3:
输入: x = 1, y = 2, target = 3 输出: true 解释:同时倒满两个水壶。现在两个水壶中水的总量等于 3。
提示:
-
1 <= x, y, target <= 103
思路分析
深度优先遍历、广度优先遍历或数学(贝祖定理)。这道题重点是如何抽象倒水壶的表示办法以及梳理清楚存在几种可能的操作。
有三种情况,八种可能的操作
-
装满任意一个水壶
-
装满 A
-
装满 B
-
-
清空任意一个水壶
-
清空 A
-
清空 B
-
-
从一个水壶向另外一个水壶倒水,直到装满或者倒空
-
A 到 B,A 剩余,B 满
-
A 到 B,A 空,B 未满
-
B 到 A,A 满,B 剩余
-
B 到 A,A 未满,B 空
-
使用 (x, y) 来表示 A 和 B 中当前的水量。
-
一刷
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
/**
* @author D瓜哥 · https://www.diguage.com
* @since 2025-07-18 22:28:36
*/
public boolean canMeasureWater(int x, int y, int target) {
if (target == 0) {
return true;
}
if (x + y < target) {
return false;
}
State init = new State(0, 0);
Queue<State> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Set<State> visited = new HashSet<>();
queue.offer(init);
visited.add(init);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
State cur = queue.poll();
int cx = cur.x;
int cy = cur.y;
if (cx == target || cy == target || cx + cy == target) {
return true;
}
List<State> next = getNextState(cx, cy, x, y);
for (State s : next) {
if (!visited.contains(s)) {
queue.offer(s);
visited.add(s);
}
}
}
return false;
}
private List<State> getNextState(int cx, int cy, int x, int y) {
List<State> result = new ArrayList<>(8);
// 外部加水,加满 A。(未满加水)
if (cx < x) {
State s1 = new State(x, cy);
result.add(s1);
}
// 外部加水,加满 B。(未满加水)
if (cy < y) {
State s2 = new State(cx, y);
result.add(s2);
}
// 把 A 清空。(有水才能清空)
if (cx > 0) {
State s3 = new State(0, cy);
result.add(s3);
}
// 把 B 清空。(有水才能清空)
if (cy > 0) {
State s4 = new State(cx, 0);
result.add(s4);
}
// 从 A 到 B,使得 B 满,A 剩余。(有剩余才倒)
if (cx - (y - cy) > 0) {
State s5 = new State(cx - (y - cy), y);
result.add(s5);
}
// 从 A 到 B, A 空,B 未满。(倒过去不满才倒)
if (cx + cy < y) {
State s6 = new State(x, cx + cy);
result.add(s6);
}
// 从 B 到 A,使得 A 满,B 剩余。(有剩余才倒)
if (cy - (x - cx) > 0) {
State s7 = new State(x, cy - (x - cx));
result.add(s7);
}
// 从 B 到 A,使得 A 未满,B 空。(倒过去不满才倒)
if (cx + cy < x) {
State s8 = new State(cx + cy, 0);
result.add(s8);
}
return result;
}
private static class State {
final int x;
final int y;
public State(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(x, y);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
State state = (State) o;
return x == state.x && y == state.y;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "State{x=" + x + ", y=" + y + "}";
}
}